|
December 2023

Update: We’re migrating Medicare Plus Blue membership to NASCO beginning in 2024
In the March and October issues of The Record, we let you know that Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan is updating its internal processes in preparation for moving its Medicare Plus Blue℠ membership to the NASCO operating system, beginning next year. This reminder article includes some additional information and updates, as well as an example of what the new voucher will look like.
The migration of Medicare Plus Blue membership to the NASCO, which will affect the look of the Medicare Plus Blue provider vouchers and member ID cards, will take place in phases. In January 2024, members of groups that are new to Medicare Plus Blue will be loaded to the operating system. Then, in January 2025, individual members and those in other select group plans will migrate to NASCO. In 2026, key and large group membership will migrate.
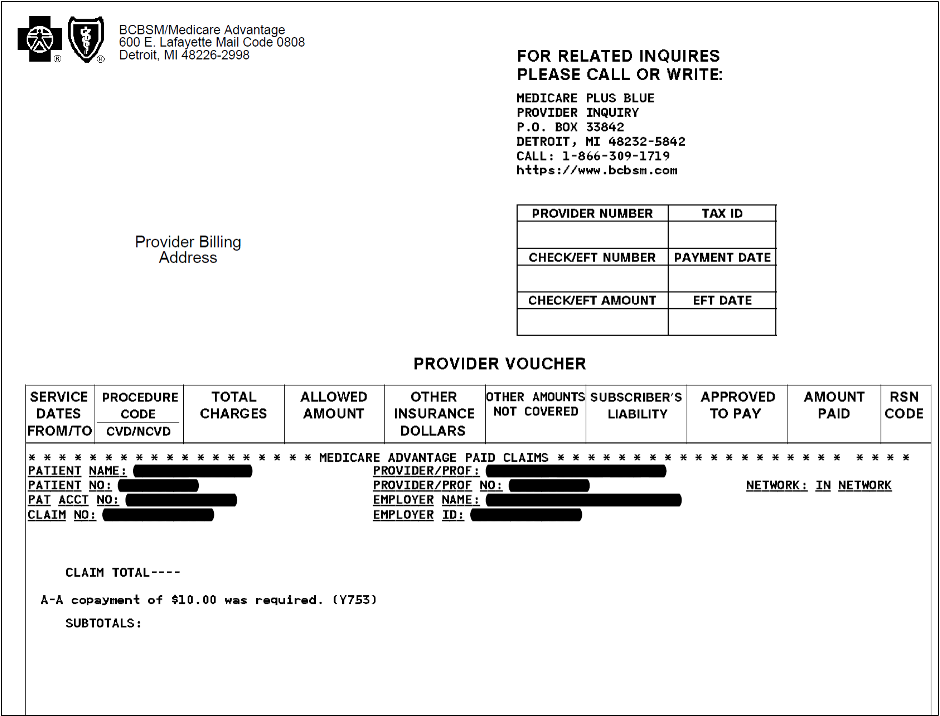
The new Medicare Plus Blue provider voucher will look similar to the current Blue Cross commercial vouchers but will include a new field that indicates the provider network and new columns to identify the tax ID and electronic funds transfer dates. The sequestration and withhold amounts will appear in the remittance advice section. Inpatient, acute or rehabilitation diagnosis-related group claims will be listed on a single line on the remittance. Outpatient claims will continue to be listed on the claim line level.
Here’s a look at what the top portion of the new voucher will look like:
Access our training site from our provider portal; new learning path available
Starting Dec. 1, our provider training site will be accessible from our provider portal, availity.com.**
To access the training site, follow these steps:
- Log in to the provider portal
- Click on Payer Spaces on the menu bar and then click on the BCBSM and BCN logo.
- Under Applications, click on the Provider Training Site tile
- Click on Submit on the Select an Organization page
- Existing users who used the same email address as their provider portal profile email will be directed to the training site. If you used a different email address, contact ProviderTraining@bcbsm.com to update your profile.
Note: If you’re a new training site user, complete the one-time registration by entering your role and creating a password. This allows you to access the training site outside of the provider portal if needed.
If you need assistance navigating the provider training site, email ProviderTraining@bcbsm.com.
New on-demand training available: Check out our new learning path
Provider Experience continues to offer training resources for health care providers and staff. Our on-demand courses are designed to help you work more efficiently with Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network. As part of our ongoing efforts, we recently added a new learning path.
Our newest learning path contains courses for medical coders, medical billing specialists and others who work with medical record documentation. This is our latest effort to help providers determine the right courses to take. We’ll keep updating the courses as new ones are created that cover coding and medical record documentation topics. This will ensure you have the latest information that’s easy to find in one spot.
Professional providers and facilities should encourage medical coders, billers and records technicians to view the new path. Simply open the Course Catalog on the provider training website and click on Learning paths.
And don’t forget to check the dashboard on our provider training site. It’s designed to enhance the training experience for providers and staff so watch for announcements as we add more courses, including those with CME offerings.
Availity® is an independent company that contracts with Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network to offer provider portal and electronic data interchange services.
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network don’t own or control this website.
Virtual Care replacing Blue Cross Online Visits in January
Beginning in 2024, eligible Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network members will no longer use Blue Cross Online Visits℠ for virtual urgent and mental health care. On Jan. 1, 2024, all members with this benefit will use Virtual Care by Teladoc Health®.
Virtual Care will be available through the Teladoc Health app and website, and by phone. Members will still have access to virtual urgent care 24/7 and mental health care by appointment, including evenings and weekends.
We understand that many health care providers offer virtual visits directly through their office. We encourage providers who don’t offer virtual visits to their patients to consider recommending Virtual Care to the Blue Cross and BCN members who express interest in it. Starting on Jan. 1, you can direct them to bcbsm.com/virtualcare or to call 1-800-835-2362, 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
View our Virtual Care FAQ for more information.
Urgent care
With Virtual Care, members have care when they need it. They can talk to a U.S. board-certified doctor when their primary care provider isn’t available about conditions such as:
- Sinus and respiratory infections
- Cold and flu
- Painful urination
- Eye irritation or redness
- Sore throat
Members can select 24/7 Care in the Teladoc Health app or call the above phone number for assistance and to schedule an appointment.
Mental health care
Members can select Mental Health in the Teladoc Health app to find and get care from licensed therapists and U.S. board-certified psychiatrists. They can also call 1-800-835-2362 to schedule an appointment. Visits are private and confidential, and provide ongoing support for stressful situations or issues such as grief, anxiety and depression.
Members can start scheduling appointments on Jan. 1. Visits are available from 7 a.m. to 9 p.m. Eastern time, seven days a week. Psychotherapy with a psychologist or clinical social worker is available for members ages 13 and older, while members ages 18 and older can receive psychiatric services. Doctors don’t prescribe controlled substances.
We encourage mental health care providers to speak with their patients who have Blue Cross and BCN health coverage about this transition and assist them with mental health strategies and resources. Share with them the Blue Cross Behavioral Health website and let them know they can call the behavioral health phone number on the back of their member ID cards for more information or if they have a behavioral health need.
Members can also log in to their Blue Cross member account at bcbsm.com or through the mobile app to use Find Care and identify a mental health care provider they may want to see. Members can use Find Care to confirm if a Blue Cross provider offers virtual visits.
Virtual Care solutions
Virtual Care is part of an array of virtual care solutions Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan is offering to members. You can read about another solution, Virtual Primary Care, in this article that’s also in this issue of the newsletter. Virtual Primary Care is available to Blue Cross PPO members.
Teladoc Health® is an independent company that provides Virtual Care Solutions for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network.
Virtual Primary Care: An optional benefit for Blue Cross commercial members starting Jan. 1
As part of an array of virtual care solutions we’re offering our members, we’re introducing a program called Virtual Primary Care to select Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan members.
Starting Jan. 1, 2024, Virtual Primary Care will be available to all Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan fully insured commercial members (and family members on their plan who are 18 and older) and as a buy-up option for other groups. The offering will be supported by Teladoc Health®, an independent company that has contracted with Blue Cross to provide virtual primary care solutions.
Unlike the Blue Care Network virtual primary care plan, which is considered a health plan product, the Blue Cross commercial solution is an optional benefit that some members may decide to use. Most of the members expected to use this benefit are those who aren’t attributed to a primary care physician and who aren’t seeking in-person care.
“Our customers, particularly the employer groups I work with, recognize the importance of a primary care relationship,” said Dr. Gretchen Goltz, medical director, Provider Engagement, in a column in the November-December issue of Hospital and Physician Update. “Many of them want all their employees to establish a care relationship with a primary care provider. At Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan, we agree with that line of thinking. We know that our members who have a primary care doctor they see regularly for preventive health care and appropriate screenings have better overall health outcomes.”
With Virtual Primary Care, members will be able to select a board-certified primary care physician by logging in to their member account, clicking on Your Choices for Care and following the prompts to the Virtual Care tab. Medical visits are with a board-certified physician and are primarily delivered by video.
Patients can also communicate with their care team by phone or in-app messaging. Those who register for Teladoc Health and schedule a first appointment will receive a blood pressure monitor and cuff.
When necessary, Teladoc Health will refer patients to specialists for in-person care. They won’t call primary care practices to refer patients to in-person care, but if a patient needs to see a PCP in person, Teladoc Health will work with the patient to find appropriate care using our Find a Doctor search tool.
For more information about our virtual care solutions
- To learn more about Virtual Primary Care, check out this flyer.
- To see how Virtual Primary Care will be reflected in Benefit Explainer, see this article, also in this issue.
- To read about the BCN virtual primary care plan, see this page of the November-December 2022 issue of BCN Provider News.
- To read about how we’re transitioning Blue Cross Online Visits℠ to Virtual Care, see this article, also in this issue.
Benefit changes coming in 2024 for UAW Retiree Medical Benefits Trust members
What you need to know
Changes are coming for certain URMBT members in January 2024. There are many reductions in deductibles, coinsurance and other cost-sharing amounts. Be sure to check benefits and eligibility.
Starting Jan. 1, 2024, there will be several changes to the UAW Retiree Medical Benefits Trust members’ health plan benefits. We’re providing a summary of those changes below.
Enhanced Care Plan, known as ECP, and Traditional Care Network, or TCN, plans:
Cost share updates for General members
- The in-network deductible is reduced to $175 for individuals and $450 for families.
- In-network coinsurance has been removed; it’s now $0.
- The in-network out-of-pocket maximum is reduced to $175 for individuals and $450 for families.
Cost share updates for Protected members
- GM and Chrysler Protected members: In-network deductibles, coinsurance and out-of-pocket maximums have been removed; they are now $0.
- GM and Chrysler Protected members: Out-of-network coinsurance is reduced to 10%.
- Ford Protected members: Out-of-network out-of-pocket maximums will be capped at $3,000 for individuals and $5,500 for families to match GM and Chrysler Protected. Currently, the out-of-pocket maximum for out-of-network services is unlimited.
Note: In 2024, the ECP and TCN Protected class plans will be aligned for all Protected members.
Office visits
- ECP members:
- In-network primary care physician, or PCP, office visit copayment is removed; it’s now $0.
- In-network specialist office visit copayment is reduced to $10.
- TCN members: Office visits are now a benefit when performed by an in-network provider.
- In-network PCP office visit copayment is $0.
- In-network specialist office visit copayment is the lesser of $10 or 20% after coordinating with Medicare.
- Additional covered office-related services that are performed as part of an office visit are payable at 100%
These office copay changes also apply to the following services:
- Office/outpatient consultation
- Outpatient presurgical consultation
- Telemedicine visit (Blue Cross provider)
- Virtual Care by Teladoc® (replaces Blue Cross Online VisitsSM)
- Advance care planning
- Routine physical/annual exam
- Gynecological exam
- Routine vision exam
- Diabetic retinopathy exam
- Well-child visit
Note: Be sure to refer to the member’s eligibility and benefits for additional coverage details.
Urgent care and retail health clinic copays
- General members: Urgent care and retail health clinic copayments are reduced to $40.
- GM and Chrysler Protected members: Urgent care and retail health clinic copayments have been removed; they are now $0.
Note: Ford Protected members currently have $0 urgent care and retail health clinic copayments.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a benefit for the treatment of chronic lower back pain only for ECP members when an individual has been referred by their treating physician to a licensed acupuncturist. Coverage is subject to the new in-network cost share described above. Services rendered by an out-of-network provider are not covered.
Blue Care Network plans
Cost share updates
- General members: The in-network deductible is reduced to $250 for an individual and $525 for families.
Office visit copays
- General members: In-network primary care provider office visit copayment is reduced to $15; the specialist office visit copayment is reduced to $25.
- Protected members: In-network primary care provider and specialist office visit copayments are reduced to $15.
Urgent care and retail health clinic copays
- General members: In-network urgent care and retail health clinic copayments are reduced to $40.
- GM and Chrysler Protected members: In-network urgent care and retail health clinic copayments are reduced to $40.
BCN Advantage℠ plans
Cost share updates
- General members: In-network deductible is reduced to $250 for individuals and $525 for families.
Office visit copays
- General members: In-network primary care provider office visit copayment is reduced to $15; the specialist office visit copayment is reduced to $25.
- Protected members: In-network primary care provider and specialist office visit copayments are reduced to $15.
Urgent care and retail health clinic copays
- General members: In-network urgent care and retail health clinic copayments are reduced to $15.
- GM and Chrysler Protected members: In-network urgent care and retail health clinic copayments are reduced to $15.
Medicare Advantage Prescription Drug, or MAPD, plans:
Cost share updates
- General members: In-network deductible, coinsurance and out-of-pocket maximum (for deductible and coinsurance services only) have been removed; they are now $0. The in-network out-of-pocket maximum of $1,500 for copay-based services still applies.
- Coinsurance applies for Part B medical drugs dispensed at a retail pharmacy or through mail-order:
- 10% coinsurance up to dollar maximum equal to copay value ($33 or prorated for days’ supply of brand medications and generic medications are payable at 100%)
Note: The $500 out-of-pocket maximum remains in place for this benefit only.
Office visit copays
- General members: In-network primary care provider office visit copayment is reduced to $0, and the specialist office visit copayment is reduced to $10.
Urgent care and retail health clinic copays
- General and Protected members: In-network urgent care and retail health clinic copayments are reduced to $15.
As always, remember to check benefits and eligibility.
New MESSA medical plan takes effect Jan. 1
The Michigan Education Special Services Association, commonly known as MESSA, is launching a new medical plan, effective Jan. 1, 2024, called MESSA Balance+.
MESSA Balance+ is a high-deductible health plan featuring copayments for office visits and coinsurance for medical services. It also comes with a prescription plan that includes a mix of copayments and coinsurance, plus an extensive list of free preventive medications. It’s eligible for a health savings account and includes MESSA’s bundle of supplemental plans — accident, critical illness and hospital indemnity.
Because of the unique out-of-pocket cost structure of MESSA Balance+, be sure to check benefits before providing services to MESSA members.
Category I RSV vaccine codes added
The American Medical Association has added CPT Category I RSV vaccine codes. The codes, effective dates and Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan’s coverage decisions are below.
Medicine vaccines/Toxoids
Code |
Change |
Coverage comments |
Effective date |
*90683 |
Added |
Covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
*90679 |
Added |
Covered |
May 3, 2023 |
None of the information included in this article is intended to be legal advice and, as such, it remains the provider’s responsibility to ensure that all coding and documentation are done in accordance with all applicable state and federal laws and regulations.
CPT Category III code update: New codes
The American Medical Association has added 45 new Category III codes as part of its CPT update. The codes, effective dates and Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan’s coverage decisions are below.
Radiology
Code |
Change |
Coverage comments |
Effective date |
0814T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0815T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0857T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
Surgery
Code |
Change |
Coverage comments |
Effective date |
0813T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0864T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
Medicine
Code |
Change |
Coverage comments |
Effective date |
0811T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0812T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
Cardiology
Code |
Change |
Coverage comments |
Effective date |
0823T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0824T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0825T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0826T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
Medicine/Psychiatric services/Other Psychotherapy
Code |
Change |
Coverage comments |
Effective date |
0820T |
Added |
Covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0821T |
Added |
Covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0822T |
Added |
Covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0858T |
Added |
Covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
Pathology and Laboratory
Code |
Change |
Coverage comments |
Effective date |
0827T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0828T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0829T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0830T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0831T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0832T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0833T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0834T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0835T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0836T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0837T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0838T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0839T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0840T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0841T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0842T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0843T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0844T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0845T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0846T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0847T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0848T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0849T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0850T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0851T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0852T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0853T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0854T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0855T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
0856T |
Added |
Not covered |
Jan. 1, 2024 |
None of the information included in this article is intended to be legal advice and, as such, it remains the provider’s responsibility to ensure that all coding and documentation are done in accordance with all applicable state and federal laws and regulations.
Billing chart: Blue Cross highlights medical, benefit policy changes
You’ll find the latest information about procedure codes and Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan billing guidelines in the following chart.
This billing chart is organized numerically by procedure code. Newly approved procedures will appear under the New Payable Procedures heading. Procedures for which we have changed a billing guideline or added a new payable group will appear under Updates to Payable Procedures. Procedures for which we are clarifying our guidelines will appear under Policy Clarifications. New procedures that are not covered will appear under Experimental Procedures.
We'll publish information about new Blue Cross groups or changes to group benefits under the Group Benefit Changes heading.
For more detailed descriptions of the Blue Cross' policies for these procedures, check under the Commercial Policy tab in Benefit Explainer on Availity®. To access this online information:
1. Log in to availity.com.
2 .Click on Payer Spaces on the Availity menu bar.
3. Click on the BCBSM and BCN logo.
4. Click on Benefit Explainer on the Applications tab.
5. Click on the Commercial Policy tab.
6. Click on Topic.
7. Under Topic Criteria, click on the circle for Unique Identifier and click the drop-down arrow next to Choose Identifier Type, then click on HCPCS Code.
8. Enter the procedure code.
9. Click on Finish.
10. Click on Search.
| Code* |
BCBSM changes to:
Basic Benefit and Medical Policy, Group
Variations Payment Policy, Guidelines
|
| NEW PAYABLE PROCEDURES |
0648T, 0649T
76391, 81596, 76981, 76982, 76983,
87467, 91200, 0002M, 0003M
Not covered
0014M, 76498,** 81599,** 84999**
**Unlisted procedures |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Evaluation or monitoring of chronic liver disease
The safety and effectiveness of ultrasonic transient elastography (FibroScan®) for the evaluation or monitoring of individuals with chronic liver disease have been established. It may be considered a useful diagnostic option when indicated.
Magnetic resonance elastography for the diagnosis and management of advanced hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis has been established. It may be considered a useful option when indicated.
Multiparametric MRI (LiverMultiScan) is considered a useful option for the diagnosis and management of advanced hepatic fibrosis/cirrhosis.
The use of FibroSURE™ multianalyte assays (HCV FibroSURE, ASH FibroSURE, NASH FibroSURE) in chronic liver disease has been established. It may be considered a useful diagnostic option when indicated.
The use of other noninvasive imaging including, but not limited to, acoustic radiation force impulse imaging, known as ARFI, or real-time tissue elastography, is considered experimental for the evaluation or monitoring of patients with chronic liver disease. While these services may be safe, their clinical utility for this clinical indication hasn’t been determined.
The peer-reviewed medical literature hasn’t demonstrated the clinical utility of other multianalyte assays with algorithmic analyses (e.g., FIBROSpect II, Enhanced Liver Fibrosis Test) for the evaluation or monitoring of patients with chronic liver disease. Therefore, these services are experimental.
Multiparametric MRI procedures are covered for members meeting criteria, effective Sept. 1, 2023.
Benefit policy:
*0648T and *0649T may be payable, effective Sept. 1, 2023.
Inclusions:
Noninvasive imaging techniques:
- Ultrasound transient elastography (FibroSCAN®), using an FDA-approved probe (e.g., S+ M+ or XL+ Probe), may be considered established for the evaluation or monitoring of chronic liver disease.
- Magnetic resonance elastography, or MRE, may be considered established for the diagnosis or management of advanced hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis for one of the following:
- Individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease who have high risk for cirrhosis due to advanced age, obesity, diabetes or alanine aminotransferase, or ALT, level more than twice the upper limit of normal.
- Individuals with other established chronic liver diseases when ultrasound elastography cannot be performed or is non-diagnostic.
- Multiparametric MRI (LiverMultiScan) is considered a useful option for the diagnosis and management of advanced hepatic fibrosis/cirrhosis when diagnostic testing such as an ultrasound is inconclusive or non-diagnostic.
Multianalyte assays:
- A FibroSURE™ multianalyte assay (either HCV FibroSURE™, ASH FibroSURE™ or NASH FibroSURE™) may be considered established for the evaluation or monitoring of chronic liver disease.
Exclusions:
Noninvasive imaging techniques:
- Ultrasound transient elastography in individuals with ascites
- Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging, or ARFI
- Real-time tissue elastography
- Use of ultrasound elastography to differentiate benign from malignant liver lesions
Multianalyte assays:
- Multianalyte assays with algorithmic analyses for the evaluation or monitoring of patients with chronic liver disease not listed above (e.g., Fibrospect, ELF, etc. – this is not a complete list)
|
64628, 64629 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
RFA of the basivertebral nerve for low back pain (Intracept®)
The safety and effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation, or RFA, of the basivertebral nerve have been established. It may be considered a useful therapeutic option when selection criteria are met. Inclusionary and exclusionary guidelines have been updated, effective Oct. 1, 2023.
Inclusions:
Basivertebral nerve ablation, with an FDA-approved device, for one or more levels of L3 through S1 when all the following are met:
- Individual is skeletally mature (18 years or older).
- Moderate to severe chronic low back pain that is primarily axiala in nature.
- Pain is refractory to at least six months of non-operative treatmentb within the past year, including at least six weeks of detailed professional directed exercise program (i.e., physical therapy)
- Type 1 or Type 2 Modic changes are noted at the vertebral bodies to be treated, on an MRI between L3 and S1.
- Type 1 – Inflammation, edema, vertebral endplate changes, disruption and fissuring of the endplate, vascularized fibrous tissues within the adjacent marrow, hypo-intensive signals.
- Type 2 – Changes to the vertebral body marrow including replacement of normal bone marrow by fat, and hyper-intensive signals.
aPain that is localized (e.g., lower back) and isn’t accompanied by motor or sensory dysfunction in the associated extremities (e.g., legs).
bPharmacological therapy (e.g., analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants), exercise, spinal manipulation, acupuncture, cognitive-behavioral therapy and physical therapy.
Note: When performing ablations for members with implanted electric devices (spinal cord stimulator, pacemaker or defibrillator, etc.), manufacturer guidelines should be followed regarding turning off or monitoring the device during the ablation procedure.
Exclusions:
- Imaging suggests other etiologies for pain including:
- Active or recurrent facet symptoms
- Disc extrusion or protrusion (>5 mm)
- Spondylolisthesis (>2 mm at any level)
- Spondylolysis at any level
- Lumbar scoliosis (> 10 degrees)
- Modic changes at any level above L3-L4
- History of spine fragility/fracture
- Osteoporosis (T-score < -2.5)
- Trauma/compression fracture
- Spinal cancer
- Imaging-confirmed spinal stenosis with neurogenic claudication (pain, numbness or weakness into the buttocks, thighs or calves, often brought on by standing or walking and relieved by flexion or sitting).
- Active or recurrent radicular pain (pain that travels along a dermatomal distribution into the lower extremity, which can be associated with numbness, weakness or tingling).
- Any prior lumbar spine surgery, other than laminectomy or discectomy > 6 months prior with resolution of radiculopathy.
- Bed bound or other condition that prevents early mobility
- BMI > 40
- Active, untreated substance/drug use disorder
- Uncontrolled moderate to severe depression, evaluated by psychiatric examination or by a validated depression screening test (e.g., Beck Depression Inventory, PHQ-9, etc.)
- Presence of severe cardiac or pulmonary compromise
- Pregnancy less than 12 months postpartum or current breastfeeding
- Active systemic infection, spine infection or bleeding diathesis
- Any current litigation related to back pain or injury
- Planned in conjunction with any other procedures or within six weeks of any prior procedure
- Repeat basivertebral ablation at the same level as a previous BVN ablation.
- Above criteria aren’t met.
|
| POLICY CLARIFICATIONS |
32850, 32851, 32852, 32853,
32854, 32855, 32856, S2060,
S2061 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Lung and lobar lung transplants
The safety and effectiveness of lung or lobar lung transplantation have been established. It may be considered a useful therapeutic option for carefully selected adults, children and adolescents with irreversible, progressively disabling, primary or secondary end-stage pulmonary disease. It’s a useful therapeutic option for individuals meeting selection guidelines.
The safety and effectiveness of lung and lobar lung re-transplantation have been established. It may be considered a useful therapeutic option for carefully selected adults, children and adolescents following an initial failed lung or lobar lung transplantation, and who meet criteria for lung transplantation. It’s a useful therapeutic option for individuals meeting selection guidelines.
Lung or lobar lung transplantation is considered experimental in all other situations.
Inclusionary criteria have been updated, effective Nov. 1, 2023.
Note: Final patient eligibility for transplant is subject to the judgment and discretion of the requesting transplant center.
Inclusions:
Lung specific-background information:
Bilateral lung transplantation is typically required when chronic lung infection disease is present, that is, associated with cystic fibrosis and bronchiectasis. Some, but not all, cases of pulmonary hypertension will require bilateral lung transplantation. Bronchiolitis obliterans is associated with chronic lung transplant rejection, and thus may be the etiology of a request for lung re-transplantation.
Indications for lung and lobar lung transplantation include, but are not limited to, irreversible, chronic lung diseases for which there is no further medical or surgical therapy available, and survival is limited. Lung transplantation is rarely an option for acutely, critically ill patients. The most common illnesses that may result in irreversible, progressively disabling, primary or secondary end-stage pulmonary disease include, but are not limited to:
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
- Asbestosis
- Benign hypertensive heart disease without congestive heart failure
- Bilateral bronchiectasis
- Bronchiolitis obliterans
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Chronic airway obstruction, not elsewhere classified
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Chronic respiratory conditions due to fumes and vapors
- Chronic respiratory disease arising in the perinatal period
- Coal workers’ pneumoconiosis
- Congenital bronchiectasis
- Cystic fibrosis with meconium ileus (double lung transplanted)
- Cystic fibrosis without mention of meconium ileus (double lung transplanted)
- Eisenmenger’s syndrome
- Emphysema
- Eosinophilic granuloma
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Idiopathic fibrosing alveolitis
- Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis
- Lung involvement in other diseases classified elsewhere
- Lymphangiomyomatosis
- Neoplasm of uncertain behavior of trachea, bronchus and lung
- Other chronic bronchitis
- Other deficiencies of circulating enzymes
- Other emphysema
- Other specified disorders of metabolism
- Pneumoconiosis due to other inorganic dust
- Pneumoconiosis due to other silica or silicates
- Pneumoconiosis, unspecified
- Pneumonopathy due to inhalation of other dust
- Post inflammatory pulmonary fibrosis
- Primary pulmonary hypertension
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Pulmonary embolism and infarction
- Pulmonary hypertension due to cardiac disease
- Recurrent pulmonary embolism
- Sarcoidosis
- Scleroderma
- Systemic sclerosis
- Tuberculosis fibrosis of lung
- Ventricular septal defect
General exclusions (contraindications):
Potential contraindications are subject to the judgment of the transplant center:
- Known current malignancy, or history of recent malignancy
- Untreated systemic infection making immunosuppression unsafe, including chronic infection
- Other irreversible end-stage disease not attributed to heart or lung disease
- Stable systemic disease that could be exacerbated by immunosuppression
- Psychosocial conditions or chemical dependency affecting the ability to adhere to therapy as defined by the transplant program
Policy specific (one of the following):
- Coronary artery disease not amenable to percutaneous intervention or bypass grafting, or associated with significant impairment of left ventricular functiona
- Colonization with highly resistant or highly virulent bacteria, fungi or mycobacteria.
aSome patients may be candidates for combined heart and lung transplantation.
The consideration for risk-reducing procedure (e.g., CABG) performed at the same time as the organ transplant is a consideration based on the medical consultation review.
Patients must meet United Network for Organ Sharing guidelines for a lung allocation score greater than zero.
Exclusions:
Patients not meeting the above inclusionary guidelines. |
38204, 38205, 38206, 38207,
38208, 38209, 38210, 38211,
38212, 38213, 38214, 38215,
38230, 38232, 38240, 38241,
S2150 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
BMT-HCT for non-Hodgkin lymphoma
The safety and effectiveness of hematopoietic cell transplantation for non-Hodgkin lymphomas, or NHL, have been established. It may be considered a useful therapeutic option for individuals meeting specific criteria.
Inclusionary and exclusionary criteria have been updated, effective Nov. 1, 2023.
Inclusionary and exclusionary guidelines:
For individuals with non-Hodgkin lymphoma B-cell subtypes considered aggressive (except mantle cell lymphoma) or mature T-cell or NK-cell (peripheral T-cell) neoplasms
Inclusions:
Either allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation, or HCT, using a myeloablative conditioning regimen or autologous HCT may be considered established when one of the following is met:
- As salvage therapy for individuals who don’t achieve a complete remission, or CR, after first-line treatment (induction) with a full course of standard-dose chemotherapy
- To achieve or consolidate a CR for those in a chemo-sensitive first or subsequent relapse
- To consolidate a first CR in individuals with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, with an age-adjusted International Prognostic Index score that predicts a high- or high-intermediate risk of relapse
- To consolidate a first CR in individuals with high-risk subtypes of mature T-cell or NK-cell (peripheral T-cell) neoplasms
Exclusions:
Individuals not meeting the above guidelines.
Mantle cell lymphoma
Inclusions:
- Autologous HCT to consolidate a first remission
- Allogeneic HCT, myeloablative or reduced-intensity conditioning, when used as salvage therapy
Exclusions:
- Autologous HCT when used as salvage therapy
- Allogeneic HCT to consolidate a first remission
For individuals with NHL B-cell subtypes considered indolent
Inclusions:
- Either allogeneic HCT using a myeloablative conditioning regimen or autologous HCT when one of the following is met:
- As salvage therapy for individuals who don’t achieve CR after first-line treatment (induction) with a full course of standard-dose chemotherapy
- To achieve or consolidate CR for those in a first or subsequent chemo-sensitive relapse, whether or not their lymphoma has undergone a transformation to a higher grade
Exclusions:
- Either autologous HCT or allogeneic HCT is considered experimental:
- As initial therapy (i.e., without a full course of standard-dose induction chemotherapy) for any NHL
- To consolidate a first CR for individuals with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and an International Prognostic Index score that predicts a low or low-intermediate risk of relapse
- To consolidate a first CR for those with indolent NHL B-cell subtypes
For individuals with hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma
Inclusions:
- Allogeneic HCT to consolidate a first CR or partial response
- Autologous to consolidate a first response if a suitable donor isn’t available for individuals who are ineligible for allogeneic HCT
Exclusions:
- Autologous or allogeneic HCT as initial therapy before the completion of the full course of induction chemotherapy
Reduced intensity conditioning allogeneic HCT
Inclusions:
Treatment of NHL in individuals who meet criteria for an allogeneic HCT but who don’t qualify for a myeloablative allogeneic HCT.
Exclusions:
- Those not meeting the above inclusionary guideline.
Tandem transplants are considered experimental to treat individuals with any stage, grade or subtype of NHL. |
47133, 47135, 47140, 47141, 47142, 47143, 47144, 47145, 47146, 47147, 47399 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Liver transplant
The safety and effectiveness of liver transplantation and retransplantation have been established. It may be considered a useful therapeutic procedure in carefully selected patients with end-stage liver failure due to irreversibly damaged livers.
Inclusionary and exclusionary criteria have been updated, effective Nov. 1, 2023.
Inclusionary and exclusionary guidelines:
Note: Liver transplants (cadaver or living donor) are covered for the indications listed below when adolescents or adults have met the requesting transplanting center’s selection criteria and one of the following:
- Model of End-stage Liver Disease, or MELD, score greater than 10 (<10 score may be considered when appropriate)
- Approval for transplant received from the United Network for Organ Sharing, or UNOS, Regional Review Board.
Inclusions for liver transplant:
- Patients with end-stage liver disease. Etiologies of end-stage liver disease include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Hepatocellular diseases
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Viral hepatitis (either A, B, C or non-A, non-B)
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
- Hemochromatosis
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
- Protoporphyria
- Wilson’s disease
- Cholestatic liver diseases
- Primary biliary cirrhosis
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis with development of secondary biliary cirrhosis
- Biliary atresia
- Vascular disease
- Neuroendocrine tumors metastatic to the liver (see NET criteria below)
- Primary hepatocellular carcinoma
- Inborn errors of metabolism
- Trauma and toxic reactions
- Miscellaneous indications
- Familial amyloid polyneuropathy
- Patients with polycystic disease of the liver who have massive hepatomegaly causing obstruction or functional impairment.
- Pediatric patients with nonmetastatic hepatoblastoma
- Patients with unresectable hilar cholangiocarcinoma if additional inclusionary criteria are met (see below).
Cholangiocarcinoma — (Available online at optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/.**
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan doesn’t own or control this website.
Note: The consideration for a risk-reducing procedure (e.g., CABG) performed at the same time as the organ transplant is a consideration based on the medical consultation review.
Criteria for liver transplant patient selection for neuroendocrine tumors, or NET, metastatic to the liver (MELD exception applications for patients with NET):
- Recipient age <60 years
- Resection of primary malignancy and extra-hepatic disease without any evidence of recurrence at least six months prior to MELD exception request.
- Liver-limited neuroendocrine liver metastasis, or NLM, bi-lobar, not amenable to resection. Tumors in the liver should meet the following radiographic characteristics:
- CT scan: Triple phase contrast
- Lesions may be seen on only one of the three phases
- Arterial phase: May demonstrate a strong enhancement
- Large lesions can become necrotic/calcified
- MRI appearance:
- Liver metastasis are hypodense on T1 and hypervascular in T2 wave images
- Diffusion restriction
- Majority of lesions are hypervascular on arterial phase with wash-out during portal venous phase IV. Hepatobiliary phase post Gadoxetate Disodium (Eovist): Hypointense lesions are characteristics of NET
- Consider for exception only those with a NET of gastro-entero-pancreatic, or GEP, origin tumors with portal system drainage. Note: Neuroendocrine tumors whose primary is located in the lower rectum, esophagus, lung, adrenal gland and thyroid aren’t candidates for automatic MELD exception.
- Lower — intermediate grade following the WHO classification. Only well differentiated (Low grade, G1) and moderately differentiated (intermediate grade G2). Mitotic rate <20 per 10 HPF with less than 20% ki-67 positive markers.
- Tumor metastatic replacement should not exceed 50% of the total liver volume
- Negative metastatic workup should include one of the following:
- Positron emission tomography, or PET, scan
- Somatostatin receptor scintigraphy
- Gallium-68 (68Ga) labeled somatostatin analogue 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododedecane-N, N′, N″,N′″-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-D-Phe1-Try3–octreotide (DOTATOC), or other scintigraphy to rule out extra-hepatic disease, especially bone metastasis.
Note: Exploratory laparotomy or laparoscopy isn’t required prior to MELD exception request.
- No evidence for extra-hepatic tumor recurrence based on metastatic radiologic workup at least three months prior to MELD exception request (submit date).
- Recheck metastatic workup every three months for MELD exception increase consideration by the Regional Review Board. Occurrence of extra-hepatic progression – for instance lymph-nodal Ga68 positive locations – should indicate de-listing. Patients may come back to the list if any extra-hepatic disease is zeroed and remained so for at least six months.
- Presence of extra-hepatic solid organ metastases (i.e., lungs, bones) should be a permanent exclusion criteria.
Exclusions for liver transplant:
- Patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma that has extended beyond the liver
- Patients with ongoing alcohol or drug abuse. (Evidence for abstinence may vary among liver transplant programs, but generally, a minimum of three months is required or enrollment in a sanctioned program.)
- Patients with conditions not included in the inclusions section.
- Severe cardiac or pulmonary disease
- AIDS
- Uncontrolled sepsis
- Anatomic abnormality that precludes liver transplantation
- Hemangiosarcoma
- Persistent noncompliance
Inclusions for liver retransplant:
Liver retransplant is established for patients with:
- Primary graft non-function
- Hepatic artery thrombosis
- Chronic rejection
- Ischemic type biliary lesions after donation after cardiac death
- Recurrent non-neoplastic disease causing late graft failure
Exclusions for liver retransplant:
Patients not meeting above inclusionary criteria for retransplant.
Potential contraindications for transplant or retransplant:
Note: Final patient eligibility for transplant is subject to the judgment and discretion of the requesting transplant center.
Potential contraindications represent situations where proceeding with transplant isn’t advisable in the context of limited organ availability. Contraindications may evolve over time as transplant experience grows in the medical community. Clinical documentation supplied to the health plan should demonstrate that attending staff at the transplant center have considered all contraindications as part of their overall evaluation of potential organ transplant recipients and have decided to proceed.
- Known current malignancy or history of recent malignancy
- Untreated systemic infection making immunosuppression unsafe, including chronic infection
- Other irreversible end-stage disease not attributed to liver disease
- Systemic disease that could be exacerbated by immunosuppression
- Psychosocial conditions or chemical dependency affecting ability to adhere to therapy as defined by the transplant program
Liver-specific guidelines/background information:
Patients with liver disease related to alcohol or drug abuse must be actively involved in a substance abuse treatment program consistent with DALLAS consensus criteria or the Sustained Alcohol Use Post-Liver Transplant, or SALT, criteria/score.
Tobacco consumption is a contraindication.
Patients with polycystic disease of the liver don’t develop liver failure but may require transplantation due to the anatomic complications of a hugely enlarged liver. The MELD/PELD score may not apply to these cases. One of the following complications should be present:
- Enlargement of liver impinging on respiratory function
- Extremely painful enlargement of liver
- Enlargement of liver significantly compressing and interfering with function of other abdominal organs
Patients with familial amyloid polyneuropathy don’t experience liver disease, per se, but develop polyneuropathy and cardiac amyloidosis due to the production of a variant transthyretin molecule by the liver. The MELD/PELD exception criteria and scores may apply to these cases. Candidacy for liver transplant is an individual consideration based on the morbidity of the polyneuropathy. Many patients may not be candidates for liver transplant alone due to coexisting cardiac disease.
Criteria used for patient selection of hepatocellular carcinoma patients eligible for liver transplant include the Milan criteria, which is considered the criterion standard, the University of California, San Francisco, or UCSF, expanded criteria, and UNOS criteria.
Notes:
Milan criteria: A single tumor 5 cm or less in diameter or 2 to 3 tumors 3 cm or less
UCSF expanded criteria: A single tumor 6.5 cm or less or up to 3 tumors 4.5 cm or less, and a total tumor size of 8 cm or less
UNOS T2 criteria: A single tumor 1 cm or greater and up to 5 cm or less in diameter or 2 to 3 tumors 1 cm or greater and up to 3 cm or less and without extrahepatic spread or macrovascular invasion. UNOS criteria, which were updated in 2013, may prioritize T2 HCC that meet specified staging and imaging criteria by allocating additional points equivalent to a MELD score predicting a 15% probability of death within three months.
Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, or HCC, are appropriate candidates for liver transplant only if the disease remains confined to the liver. Therefore, the patient should be periodically monitored while on the waiting list, and if metastatic disease develops, the patient should be removed from the transplant waiting list. In addition, at the time of transplant, a backup candidate should be scheduled. If locally extensive or metastatic cancer is discovered at the time of exploration prior to hepatectomy, the transplant should be aborted, and the backup candidate scheduled for transplant.
Note: Liver transplantation for those with T3 HCC isn’t prohibited by UNOS guidelines, but these patients don’t receive any priority on the waiting list. All patients with HCC awaiting transplantation are reassessed at three-month intervals. Those whose tumors have progressed and are no longer T2 tumors will lose the additional allocation points.
Additionally, nodules identified through imaging of cirrhotic livers are given a class 5 designation. Class 5B and 5T nodules are eligible for automatic priority. Class 5B criteria consist of a single nodule 2 cm or larger and up to 5 cm (T2 stage) that meets specified imaging criteria. Class 5T nodules have undergone subsequent locoregional treatment after being automatically approved on initial application or extension. A single class 5A nodule (>1 cm and <2 cm) corresponds to T1 HCC and doesn’t qualify for automatic priority. However, combinations of class 5A nodules are eligible for automatic priority if they meet stage T2 criteria. Class 5X lesions are outside of stage T2 and aren’t eligible for automatic exception points. Nodules less than 1 cm are considered indeterminate and aren’t considered for additional priority. Therefore, the UNOS allocation system provides strong incentives to use locoregional therapies to downsize tumors to T2 status and to prevent progression while on the waiting list.
HIV-positive patients who meet the following criteria, as stated in the 2001 guidelines of the American Society of Transplantation, could be considered candidates for liver transplantation:
- CD4 count >200 cells per cubic millimeter for >6 months
- Undetectable HIV-1 RNA
- On stable antiretroviral therapy >3 months
- No other complications from AIDS (e.g., opportunistic infection, including aspergillus, tuberculosis, coccidioidomycosis, resistant fungal infections, Kaposi sarcoma, other neoplasm)
- Meeting all other criteria for transplantation
Cholangiocarcinoma:
According to the OPTN policy on liver allocation, candidates with cholangiocarcinoma, or CCA, meeting the following criteria will be eligible for a MELD/PELD exception with a 10% mortality equivalent increase every three months:
- Centers must submit a written protocol for patient care to the OPTN/UNOS Liver and Intestinal Organ Transplantation Committee before requesting a MELD score exception for a candidate with CCA. This protocol should include selection criteria, administration of neoadjuvant therapy before transplantation, and operative staging to exclude patients with regional hepatic lymph node metastases, intrahepatic metastases or extrahepatic disease. The protocol should include data collection as deemed necessary by the OPTN/UNOS Liver and Intestinal Organ Transplantation Committee.
- Candidates must satisfy diagnostic criteria for hilar CCA: malignant-appearing stricture on cholangiography and one of the following: carbohydrate antigen 19-9 100 U/mL, or and biopsy or cytology results demonstrating malignancy, or aneuploidy. The tumor should be considered unresectable on the basis of technical considerations or underlying liver disease (e.g., primary sclerosing cholangitis).
- If cross-sectional imaging studies (computed tomography scan, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging) demonstrate a mass, the mass should be less than 3 cm.
- Intra- and extrahepatic metastases should be excluded by cross-sectional imaging studies of the chest and abdomen at the time of initial exception and every three months before score increases.
- Regional hepatic lymph node involvement and peritoneal metastases should be assessed by operative staging after completion of neoadjuvant therapy and before liver transplantation. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided aspiration of regional hepatic lymph nodes may be advisable to exclude patients with obvious metastases before neoadjuvant therapy is initiated.
- Transperitoneal aspiration or biopsy of the primary tumor (either by endoscopic ultrasound, operative, or percutaneous approaches) should be avoided because of the high risk of tumor seeding associated with these procedures.
Donor criteria: Living donor liver transplant
Donor morbidity and mortality are prime concerns in donors undergoing right lobe, left lobe or left lateral segment donor partial hepatectomy as part of living-donor liver transplantation. Partial hepatectomy is a technically demanding surgery, the success of which may be related to the availability of an experienced surgical team. In 2000, the American Society of Transplant Surgeons proposed the following guidelines for living donors:
- Should be healthy individuals who are carefully evaluated and approved by a multidisciplinary team, including hepatologists and surgeons, to ensure that they can tolerate the procedure
- Should undergo an evaluation to ensure that they fully understand the procedure and associated risks
- Should be of legal age and have sufficient intellectual ability to understand the procedures and give informed consent
- Should be emotionally related to the recipients
- Must be excluded if the donor is felt or known to be coerced
- Needs to have the ability and willingness to comply with long-term follow-up
|
52441, 52442 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Prostatic urethral lift for treatment of BPH
The safety and efficacy of the prostatic urethral lift procedure for the treatment of benign prostatic hypertrophy, or BPH, have been established. It’s a useful therapeutic option for men with symptomatic BPH who have failed conventional pharmacologic therapy.
Exclusionary criteria have been updated, effective Nov. 1, 2023.
Inclusions:
Candidates for the prostatic urethral lift procedure must meet all of the following guidelines:
- Age 45 years or older
- A documented diagnosis of symptomatic benign prostatic hypertrophy of the lateral lobes of the prostate including, but not limited to, the following symptoms:
- Difficulty starting and stopping urination (hesitancy and straining)
- Decreased strength of the urine stream (weak flow)
- Dribbling after urination
- Feeling that the bladder isn’t completely empty
- An urge to urinate again soon after urinating (urgency)
- Pain during urination (dysuria)
- Nocturia – waking up several times during the night with the urge to urinate
- Frequent urinary tract infections secondary to urinary obstruction
- Documented failure, inability to tolerate or undesirable side effects of pharmacologic intervention for BPH, including but not limited to:
- Alpha blockers, such as Uroxatral, Cardura, Rapaflo, Flomax or Hytrin
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors for BPH, such as Avodart or Proscar
- Combination drugs using both an alpha blocker and a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor
Exclusions:
- Patients not meeting the patient selection criteria above.
- Repeat procedure
|
Established
69930, 92601, 92602, 92603, 92604, 92605, 92606, 92607, 92608, 92609, 92618, L7510, L8614, L8615, L8616, L8617, L8618, L8619, L8621, L8622, L8623, L8624, L8625, L8627, L8628, L8629 |
Basic benefit and medical policy Cochlear implant
The safety and effectiveness of U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved bilateral and unilateral cochlear implants and associated hybrid cochlear implant devices have been established. The implants may be considered useful therapeutic options when indicated.
Inclusionary criteria have been updated, effective Nov. 1, 2023.
Inclusions:
Unilateral or bilateral cochlear implantation with an FDA-approved cochlear implant is considered an established, safe and effective therapy for individuals who are 9 months or older and who meet one of the following criteria:
- Unilateral or bilateral moderate to profound pre- or post-lingual sensorineural hearing loss
- Limited or no benefit from hearing aids, defined as an aided monosyllabic word score of less than or equal to 50% correct in the ear to be implanted
Replacement of internal or external components in a small subset of members may be considered established when all of the following are met:
- There is an inadequate response to existing components to the point of one of the following:
- Interfering with the individual’s activities of daily living
- The component or components are no longer functional and can’t be repaired
- Copies of original medical records must be submitted either hard copy or electronically to support medical necessity.
Cochlear implant with a hybrid device that includes the hearing aid integrated into the external sound processor of the cochlear implant (e.g., the Nucleus® Hybrid L24 Cochlear Implant System) may be considered established for patients 18 years and older who meet all the following criteria:
- Bilateral severe-to-profound high-frequency sensorineural hearing loss with residual low-frequency hearing sensitivity
- Receive limited benefit from appropriately fit bilateral hearing aids
- Have all the following hearing thresholds:
- Low-frequency hearing thresholds no poorer than 60 dB hearing level up to and including 500 Hz (averaged over 125, 250, and 500 Hz) in the ear selected for implantation
- Severe to profound mid-to-high frequency hearing loss (threshold average of 2000, 3000, and 4000 Hz ≥75 dB hearing level) in the ear to be implanted
- Moderately severe to profound mid-to-high frequency hearing loss (threshold average of
- 2000, 3000, and 4000 Hz ≤ 60 dB hearing level) in the contralateral ear
- Aided consonant-nucleus-consonant word recognition score from 10% to 60% in the ear to be implanted in the preoperative aided condition and in the contralateral ear will be equal to or better than that of the ear to be implanted but not more than 80% correct.
In certain situations, implantation consideration may be given before 9 months of age. One scenario post meningitis when cochlear ossification may preclude implantation. Another is in cases with a strong family history, because establishing a precise diagnosis is less uncertain. However, these aren’t the only examples where consideration may be given.
Cochlear implantation outside these guidelines may also be considered medically necessary if the patient is diagnosed with auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder with limited or no benefit from hearing aids.
Contraindications to cochlear implantation may include deafness due to lesions of the eighth cranial (acoustic) nerve, central auditory pathway or brainstem; active or chronic infections of the external or middle ear, and mastoid cavity or tympanic membrane perforation. Cochlear ossification may prevent electrode insertion, and the absence of cochlear development as demonstrated on computed tomography scans remains an absolute contraindication.
Exclusions:
- Upgrades of an existing, functioning external system to achieve aesthetic improvement, such as smaller profile components or a switch from a body-worn, external sound processor to a behind-the-ear model
- Replacement of internal or external components solely for the purpose of upgrading to a system with advanced technology or to a next-generation device
- Non-FDA-approved devices or indications
|
81518, 81519, 81520, 81521, 81522, 81523
Experimental
81599,** 84999,** S3854,*** 0045U, 0153U
**Not otherwise classified code (e.g., used to represent DCISionRT)
***When used to represent any gene panel test that isn’t in the “Established code” section |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Gene expression assay testing in tumor tissue for treatment guidance for breast cancer patients
The safety and effectiveness of reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction, or RT-PCR assays (i.e., Oncotype DX®, EndoPredict®, Breast Cancer Index®, MammaPrint® and Prosigna®) for determining whether to undergo adjuvant chemotherapy may be considered established. They are useful diagnostic tests for predicting the likelihood of early cancer recurrence (0 to 5 years) in individuals who meet the inclusionary guidelines.
The safety and effectiveness of the Breast Cancer Index for prognosis of late (years 5 to 10) distant recurrence, to determine the need for extended adjuvant endocrine therapy, may be considered established.
The use of other assays (i.e., Oncotype DX, EndoPredict, MammaPrint and Prosigna; this isn’t an all-inclusive list) to determine the prognosis of late (years 5 to 10) distant recurrence, to determine extended endocrine therapy, is considered experimental.
Other genetic testing for determining the likelihood of distant cancer recurrence in women is experimental (refer to policy exclusions).
Exclusionary criteria have been updated, effective Nov. 1, 2023.
Inclusions:
Testing for recurrence risk and adjuvant chemotherapy
Node-negative breast cancer
Inclusions (must meet all):
The use of Oncotype Dx, EndoPredict, MammaPrint, Breast Cancer Index and Prosigna tests to determine recurrence risk for deciding whether to undergo adjuvant chemotherapy may be considered established in women with node-negative breast cancer meeting all the following characteristics:
- Unilateral tumor
- Hormone receptor-positive (i.e., estrogen-receptor positive or progesterone-receptor positive)
- Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative
- Tumor size 0.6-1 cm with moderate or poor differentiation or unfavorable features or tumor size larger than 1 cm
- Node negative (lymph nodes with micrometastases [less than or equal to 2 mm in size] are considered node negative for this policy).
- Who will be treated with adjuvant endocrine therapy (i.e., tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors)
- When the test result will aid the patient in making the decision regarding chemotherapy (i.e., when chemotherapy is a therapeutic option)
- When ordered within six months after diagnosis, since the value of the test for making decisions regarding delayed chemotherapy is unknown
Node-positive breast cancer with one to three nodes positive using Oncotype DX, EndoPredict, Breast Cancer Index or Prosigna
Inclusions:
The use of Oncotype Dx, EndoPredict, Breast Cancer Index and Prosigna tests to determine recurrence risk for deciding whether to undergo adjuvant chemotherapy may be considered established in women with N1 breast cancer meeting all the following criteria:
- Hormone receptor-positive (i.e., estrogen-receptor positive)
- Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative
- N1 (< 4 nodes positive)
- When ordered within six months after diagnosis
Node-positive breast cancer with one to three nodes positive using MammaPrint
Inclusions:
The use of the MammaPrint assay to determine recurrence risk for deciding whether to undergo adjuvant chemotherapy may be considered medically necessary in women with primary, invasive breast cancer meeting all the following characteristics:
- Unilateral tumor
- Hormone receptor-positive (i.e., estrogen-receptor positive or progesterone-receptor positive)
- Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative
- Stage T1 or T2 or operable T3 at high clinical risk**
- One to three positive nodes who will be treated with adjuvant endocrine therapy (e.g., tamoxifen, aromatase inhibitors)
- When the test result aids the patient in deciding on chemotherapy (i.e., when chemotherapy is a therapeutic option)
- When ordered within six months after diagnosis because the value of the test for making decisions regarding delayed chemotherapy is unknown
**High risk:
- Grade: Well differentiated; tumor size, 2.1 cm to 5 cm
- Grade: Moderately differentiated; tumor size, any size
- Grade: Poorly differentiated or undifferentiated; tumor size, any size
Extended endocrine therapy
Inclusions:
The Breast Cancer Index test may be considered established to predict the benefit of extended (5 to 10 years) endocrine therapy in women who are recurrence-free at five years.
Exclusions:
- Use of more than one gene expression assay for determining recurrence risk for deciding whether to undergo adjuvant chemotherapy (e.g., Oncotype Dx and MammaPrint for the same individual to help determine if adjuvant chemotherapy would be beneficial)
- Use of assays (e.g., Oncotype DX DCIS, DCISionRT®; this list isn’t all-inclusive) in women who have ductal carcinoma in situ, or DCIS, for decision-making regarding treatment planning after excisional surgery, including radiotherapy, is considered experimental.
- The use of gene expression assays in men with breast cancer is considered experimental.
- The use of gene expression assays to molecularly subclassify breast cancer (e.g., BluePrint) is considered experimental.
- The use of Insight TNBCtype™ to aid in making decisions regarding neoadjuvant chemotherapy in women with triple-negative breast cancer is considered investigational.
- Extended endocrine therapy testing other than the Breast Cancer Index.
|
84145 |
Basic benefit and medical policy Procalcitonin testing
The safety and effectiveness of procalcitonin testing, or PCT, for confirmation and monitoring of bacterial infections and sepsis in initiating or discontinuing antibiotics in specified patient populations have been established.
The medical policy statement and inclusionary and exclusionary criteria have been updated, effective Nov. 1, 2023.
Inclusionary and exclusionary guidelines:
Inclusions:
For use in the adult and pediatric population in the inpatient/emergency department setting for the following conditions:
- For use in individuals with lower respiratory tract infections (e.g., pneumonia) for initiating or discontinuing antibiotic therapy
- For use in critically ill individuals with sepsis as a guidance for discontinuation of antibiotic therapy
Exclusions:
The use of procalcitonin testing for the following conditions is experimental because of insufficient evidence of its effectiveness. Note: This isn’t an all-inclusive list.
These indications include the following diagnoses of:
- Surgical infections (including monitoring of the infection)
- Appendicitis
- Chronic renal insufficiency
- Infective endocarditis
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Parapneumonic pleural effusions
- Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
- Pancreatitis
- Pyelonephritis
It’s also considered experimental for:
- Measuring the differentiation of infection from other inflammatory complications following stem cell transplantation
- Predicting outcomes in people with acute coronary syndrome
- Prediction of neurological deficits following carotid endarterectomy
|
87389 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
*87389 added to the Physician Office Laboratory List
The procedure code *87389 was added to the Physician Office Laboratory List. It can be performed in a physician’s office. |
Established
92652, 92653, 95829, 95867, 95868, 95925, 95926, 95927, 95938, 95940, 95955, G0453
Experimental
95907, 95908, 95909, 95910, 95911, 95912, 95913, 95928, 95929, 95930, 95939, 95941, 95999 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring
Intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring, which includes somatosensory-evoked potentials, motor-evoked potentials using transcranial electrical stimulation, brainstem auditory-evoked potentials, EMG of cranial nerves, EEG and electrocorticography, is established during spinal, intracranial or vascular procedures.
Intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve is established for individuals meeting inclusionary guidelines.
Intraoperative monitoring of visual-evoked potentials is considered experimental.
Intraoperative monitoring of motor-evoked potentials using transcranial magnetic stimulation is considered experimental.
Inclusionary criteria have been updated, effective Nov. 1, 2023.
Inclusions:
The following types of intraoperative monitoring are appropriate when performed during spinal, intracranial or vascular surgeries or procedures:
- Somatosensory-evoked potentials
- Motor-evoked potentials using transcranial electrical stimulation
- Brainstem auditory-evoked potentials
- Electromyogram, or EMG, of cranial nerves
- Electroencephalogram, or EEG
- Electrocorticography, or ECoG
Notes:
- Only qualified people can perform this type of monitoring.
- Train-of-four monitoring is considered integral (not separately payable) to intraoperative procedures to measure the strength of anesthetic neuromuscular blockade.
Intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve is established in individuals undergoing:
- High-risk thyroid or parathyroid surgery, including:
- Total thyroidectomy
- Repeat thyroid or parathyroid surgery
- Surgery for cancer
- Thyrotoxicosis
- Retrosternal or giant goiter
- Thyroiditis
- Anterior cervical spine surgery associated with any of the following increased risk situations:
- Prior anterior cervical surgery, particularly revision anterior cervical discectomy and fusion, revision surgery through a scarred surgical field, reoperation for pseudarthrosis or revision for failed fusion
- Multilevel anterior cervical discectomy and fusion
- Preexisting recurrent laryngeal nerve pathology, when there is residual function of the recurrent laryngeal nerve
Exclusions:
- Intraoperative monitoring of visual-evoked potentials
- Intraoperative monitoring of motor-evoked potentials using transcranial magnetic stimulation
- Intraoperative EMG and nerve conduction velocity monitoring during surgery on the peripheral nerves
- Intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve during anterior cervical spine surgery not meeting the criteria above or during esophageal surgeries
- Intraoperative monitoring performed during any surgical procedure not specified in the inclusions
|
Procedure codes
98940, 98941, 98942, 98943, 98925, 98926, 98927, 98928, 98929
Revenue code
0531 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Chiropractic and osteopathic manipulation benefits
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan has updated its chiropractic and osteopathic manipulation benefits. The updates combined outpatient facility and professional member accumulation visit maximums and cost share. The alignment of the benefits will allow Blue Cross to adapt to the growing changes in provider billing practices. The changes will ensure compliance with benefit plan designs for our groups and will consistently apply benefit experiences regardless of where services are rendered. Claims will continue to deny manipulation services when a group doesn’t have chiropractic or osteopathic benefits.
When an outpatient facility and professional claim is reported in Place of Service 2 (outpatient hospital) for the same encounter on the same date of service, the accumulated service will count only as one visit toward the member’s benefit maximum. If a member receives an additional manipulation on the same date in a different POS 3 (office), the visit will be accumulated as a separate visit toward the member’s visit maximum.
Professional and facility existing group cost share will not change. Services performed in a facility setting will apply facility cost share and services performed in an office setting will apply an office cost share.
Payment policy:
Revenue code 0531 was turned on to accommodate the billing and reimbursement of osteopathic manipulations, when reported with a valid CPT code. This revenue code will apply fee-based reimbursement for the applicable codes.
These changes apply to all Blue Cross commercial fully insured and self-funded groups, except groups that don’t have chiropractic and osteopathic benefits. The updates are effective for all applicable groups and dates of service on and after Sept. 1, 2023. |
A4230, A4232, A4224, A4225, A4226, A9274, E0784, E0787, S1034, S1035, S1036, S1037, 0740T, 0741T |
Basic benefit and medical policy Artificial pancreas devices
The safety and effectiveness of FDA-approved artificial pancreas device systems with a low glucose suspend feature and hybrid closed loop systems may be considered established in patients with insulin-requiring diabetes who meet specified patient selection criteria. It’s a useful therapeutic option for selected patients.
The safety and effectiveness of an FDA-approved closed loop insulin delivery system (e.g., iLet bionic pancreas) may be considered established in individuals with Type 1 diabetes who meet specified patient selection criteria. It’s a useful therapeutic option for selected patients.
The safety and effectiveness of an FDA-approved insulin guidance system (e.g., D-Nav) as an aid in optimizing glycemic control may be considered established for individuals with insulin-dependent Type 2 diabetes. It’s a useful therapeutic option for selected patients.
The medical policy statement and inclusionary and exclusionary criteria have been updated, effective Nov. 1, 2023.
Inclusionary and exclusionary guidelines:
Inclusions:
Use of FDA-cleared or approved artificial pancreas device systems with a low-glucose suspend feature may be considered established in patients with insulin-requiring diabetes who meet all of the following criteria:
- Age 6 or older
- Insulin-requiring diabetes
- A history of one level 3 (glucose < 54 mg/dl [3.0mmol/L]) hypoglycemic event characterized by altered mental or physical state requiring third-party assistance for treatment of hypoglycemia (i.e., hypoglycemia unawareness) or recurrent level 2 (glucose < 54 mg/dl [3.0mmol/L]) hypoglycemic events despite multiple attempts to adjust medications or modify the diabetes treatment plan (e.g., nocturnal hypoglycemia)
Use of an FDA-cleared or approved automated insulin delivery system (artificial pancreas device system) designated as hybrid closed loop insulin delivery system (with low glucose suspend and suspend before low features) is considered established in patients with insulin requiring diabetes who meet all of the following criteria:
- Age 6 and older
- Insulin-requiring diabetes
- A history of one level 3 (glucose < 54 mg/dl [3.0mmol/L]) hypoglycemic event characterized by altered mental and/or physical state requiring third-party assistance for treatment of hypoglycemia (i.e., hypoglycemia unawareness or recurrent level 2 (glucose < 54 mg/dl [3.0mmol/L]) hypoglycemic events despite multiple attempts to adjust medications or modify the diabetes treatment plan (e.g., nocturnal hypoglycemia)
Or
- Age 2 to 6 years
- Clinical diagnosis of Type 1 diabetes for three months or more
- Glycated hemoglobin level <10.0%
- Minimum daily insulin requirement (total daily dose) of greater than or equal to 8 units
Use of an FDA-cleared or approved automated insulin delivery system (artificial pancreas device system) designated as a closed-loop insulin delivery system may be considered established in individuals with Type 1 diabetes who meet all of the following criteria:
- Age 6 years and older
- Clinical diagnosis of Type 1 diabetes for 12 months or more
- Using insulin for at least 12 months
- Diabetes managed using the same regimen (either pump or multiple daily injections, with or without continuous glucose monitoring) for three months or longer
Exclusions:
- Use of an artificial pancreas device system is considered experimental in all other situations.
- Use of an artificial pancreas device system not cleared or approved by the FDA is experimental
|
C9399
J3490
J3590 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Omisirge (omidubicel-onlv)
Omisirge (omidubicel-onlv) is considered established, effective April 17, 2023.
Coverage of Omisirge (omidubicel-onlv) is provided when all the following are met:
- Used for the FDA-approved indication
- Must be FDA-approved age
- Must have an approval for stem cell transplant on file through the Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan’s and Blue Care Network’s Human Organ Transplant Program
- Umbilical cord blood unit human leukocyte antigen-matched at four or more loci
- Must not have any of the following:
- A matched sibling or matched unrelated adult donor
- A prior allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplant
- Marked or 3+ bone marrow fibrosis
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- Must not have received prior treatment with Omisirge or any other modified allogeneic hematopoietic progenitor cell therapy derived from cord blood for the treatment of hematologic malignancies
- Trial and failure, contraindication or intolerance to the preferred drugs as listed in Blue Cross’ or BCN’s utilization management medical drug list
Quantity limitations, authorization period and renewal criteria:
- Quantity limits: Align with FDA-recommended dosing
- Authorization period: Three months
- Renewal criteria: Not applicable as no further authorization will be provided
This drug isn’t a benefit for URMBT.
|
H0031, H0032, H2014, H2019, S5108, S5111, 0362T, 0373T, 97151, 97152, 97153, 97154, 97155, 97156, 97157, 97158 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Autism spectrum disorders
The effectiveness of treatment for autism spectrum disorder has been established. It may be a useful therapeutic option when inclusionary and certificate guidelines are met.
Inclusionary and exclusionary criteria have been updated, effective Nov. 1, 2023.
Inclusions:
- Full diagnostic criteria for autism spectrum disorder, as published in the most recent edition of the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, are met.
- The maladaptive behavior must affect the individual’s personal safety, the safety of others within the individual’s environment or must significantly interfere with the individual’s ability to function.
- Services in Michigan must be provided or supervised by one of the following:
- A clinician who is a licensed behavior analyst, or LBA
- A psychiatrist who has the appropriate training
- A licensed psychologist who has the appropriate education, training and experience
- A person who holds a license, certificate or registration that authorizes them to perform services included in applied behavior analysis
Services outside of Michigan must be provided by a clinician who meets their state requirements to provide ABA therapy.
- Interventions:
- Are individually centered
- Define target behaviors
- Record objective measures of baseline levels and progress
- Identify and documents specific interventions and techniques
- Document transitional and discharge plans
Exclusions:
- Individuals who don’t meet the diagnostic criteria based on the most recent criteria by the American Psychiatric Association (i.e., most current version of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual)
- In Michigan, therapy delivered or supervised by clinicians who aren’t licensed behavior analysts or those who don’t meet state requirements to provide ABA therapy
- Outside of Michigan, therapy delivered or supervised by clinicians who don’t meet their state requirements to provide ABA therapy
Autism services allowed via telemedicine synchronous care:
- Specific autism services allowed via telemedicine synchronous care are noted in the CPT section.
- Adaptive behavior interventions (*97153) are allowed if the individual meets appropriateness criteria:
- At a minimum, the individual should exhibit basic skills of joint attention, basic discrimination, basic echoic and basic motor imitation. The individual should be able to follow common one-step instructions, participate in sessions with limited caregiver assistance and sit independently at a computer or tablet for 8 to 10 minutes. Safety concerns and challenging behaviors must be minimal.
- For complete guidelines to consider, see the document titled Guidelines for autism interventions delivered via telemedicine. Autism services provided via telemedicine may not be effective for all individuals. When services are provided via telemedicine and the individual doesn’t show progress, it is expected that the interventions would be modified to face-to-face interactions.
Autism services delivered via telemedicine are synchronous care only; asynchronous care isn’t appropriate for autism services. |
J0178 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Eylea (aflibercept)
Eylea (aflibercept) is covered for the following updated FDA-approved indication, effective Feb. 8, 2023:
- Retinopathy of prematurity
|
J1741 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Caldolor (ibuprofen injection)
The FDA has updated the indications for Caldolor (ibuprofen injection). This was effective May 11, 2023.
Caldolor is indicated in adults and pediatric patients aged 3 months and older for the management of mild to moderate pain and the management of moderate to severe pain as an adjunct to opioid analgesics. It’s also approved for the reduction of fever.
Dosage and administration:
Pediatric (pain and fever) aged 3 months to less than 6 months: 10 mg/kg intravenously over 10 minutes up to a maximum single dose of 100 mg |
J3490
J3590 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Brixadi (buprenorphine)
Brixadi (buprenorphine) is considered established when criteria are met, effective May 23, 2023.
Brixadi contains buprenorphine, a partial opioid agonist.
Brixadi is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe opioid use disorder in patients who have initiated treatment with a single dose of a transmucosal buprenorphine product or who are already being treated with buprenorphine.
Brixadi should be used as part of a complete treatment plan that includes counseling and psychosocial support.
Dosage and administration:
- Only health care providers should prepare and administer Brixadi.
- Brixadi (weekly) and Brixadi (monthly) are different formulations. Doses of Brixadi (weekly) can’t be combined to yield an equivalent Brixadi (monthly) dose.
- Brixadi should be injected slowly, into the subcutaneous tissue of the buttock, thigh, abdomen or upper arm.
- Strongly consider prescribing naloxone at the time Brixadi is initiated or renewed because patients being treated for opioid use disorder have the potential for relapse, putting them at risk for opioid overdose.
- Injection sites for Brixadi (weekly) should be alternated/rotated for each injection.
Dosage forms and strengths:
Brixadi is a weekly and monthly injection provided in a pre-filled single dose syringe with a 23 gauge ½ inch needle.
- Brixadi (weekly) is available in 8 mg/0.16 mL, 16 mg/0.32 mL, 24 mg/0.48 mL, and 32 mg/0.64 mL.
- Brixadi (monthly) is available in 64 mg/0.18 mL, 96 mg/0.27 mL, and 128 mg/0.36 mL.
Brixadi (buprenorphine) isn’t a benefit for URMBT. |
J3490
J3590 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Cyfendus (anthrax vaccine adsorbed, adjuvanted)
Cyfendus (anthrax vaccine adsorbed, adjuvanted) is considered established, effective July 20, 2023.
Cyfendus (anthrax vaccine adsorbed, adjuvanted) is a vaccine indicated for post-exposure prophylaxis of disease following suspected or confirmed exposure to Bacillus anthracis in people ages 18 through 65 when administered in conjunction with recommended antibacterial drugs.
The efficacy of Cyfendus for post-exposure prophylaxis is based solely on studies in animal models of inhalational anthrax.
Dosage and administration:
For intramuscular injection only.
Administer two doses (0.5 mL each) intramuscularly two weeks apart.
Dosage forms and strengths:
Suspension for injection; each dose is 0.5 mL.
This drug isn’t a benefit for URMBT. |
J3490
J3590 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Dengvaxia (dengue tetravalent vaccine, live)
The FDA approved new indications for Dengvaxia (dengue tetravalent vaccine, live). This was effective July 7, 2023.
- Dengvaxia is approved for use in individuals ages 6 through 16 with laboratory confirmed previous dengue infection and living in endemic areas.
Limitations of use:
Dengvaxia (dengue tetravalent vaccine, live) isn’t approved for use in individuals younger than 6 years of age. |
J3490
J3590 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Elevidys (delandistrogene moxeparvovec-rokl)
Elevidys (delandistrogene moxeparvovec-rokl) is considered experimental. This policy is effective June 22, 2023. |
J7297 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Liletta (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system)
The FDA updated the indications for Liletta (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system). This was effective June 29, 2023.
Liletta (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) is a progestin-containing intrauterine system indicated for the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding for up to five years in patients who choose intrauterine contraception as their method of contraception. |
J9177 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Padcev (enfortumab vedotin-ejfv)
Effective April 3, 2023, Padcev (enfortumab vedotin-ejfv), procedure code J9177, is payable for the following indication:
- Padcev (enfortumab vedotin-ejfv) is a Nectin-4-directed antibody and microtubule inhibitor conjugate indicated in combination with pembrolizumab for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer who aren’t eligible for cisplatin-containing chemotherapy. This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on tumor response rate and durability of response. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in the confirmatory trials.
Dosage information:
The recommended dose of Padcev (enfortumab vedotin-ejfv) in combination with pembrolizumab is 1.25 mg/kg (up to a maximum dose of 125 mg) given as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes on Days 1 and 8 of a 21-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. |
J9271 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Keytruda (pembrolizumab)
Effective April 3, 2023, Keytruda (pembrolizumab) is payable for the following indications:
Urothelial carcinoma:
- In combination with enfortumab vedotin, for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma who aren’t eligible for cisplatin-containing chemotherapy
- As a single agent for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma who aren’t eligible for any platinum-containing chemotherapy, or who have disease progression during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy or within 12 months of neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment with platinum-containing chemotherapy
- As a single agent for the treatment of patients with Bacillus Calmette-Guerin-unresponsive, high-risk, non-muscle invasive bladder cancer with carcinoma in situ with or without papillary tumors who are ineligible for or have elected not to undergo cystectomy
Microsatellite instability-high or mismatch repair deficient cancer:
- For the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with unresectable or metastatic microsatellite instability-high or mismatch repair deficient solid tumors, as determined by an FDA-approved test, that have progressed following prior treatment and who have no satisfactory alternative treatment options
|
J9312
Q5115
Q5119
Q5123 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Rituxan (rituximab)
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan has approved payment for the off-label use of Rituxan (rituximab) to treat unspecified nephritic syndrome with diffuse membranous glomerulonephritis.
URMBT groups are excluded from this change. |
| EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES |
30117, 30999,** 31299,** C9771
**Not otherwise classified code |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Ablation for chronic rhinitis (ClariFix®, RhinAer™)
Cryoablation, radiofrequency ablation and laser ablation for chronic rhinitis (allergic or nonallergic) are considered experimental, effective Nov. 1, 2023. There is insufficient evidence in the peer-reviewed medical literature to determine that it improves health outcomes. |
None of the information included in this billing chart is intended to be legal advice and, as such, it remains the provider’s responsibility to ensure that all coding and documentation are done in accordance with all applicable state and federal laws and regulations.

The PGIP evolution: New and revised participation and quality expectations
As the Physician Group Incentive Program enters its 20th year, we’re supporting the ongoing development of stronger systems of care, resulting in better clinical outcomes for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan members and Michigan residents. The goals are to see our members in high-performing care relationships and our health care providers well-supported by their PGIP physician organizations, which will allow them to deliver the transformed models and improved quality outcomes we expect.
As we work toward raising the bar, Blue Cross will continue to review and elevate our expectations, PGIP physician organization eligibility requirements and associated incentives. We’re also working to ensure the program, POs and practices continue to excel so Blue Cross members and customers receive the highest quality and most cost-effective care possible.
Eligibility requirements
Here are the eligibility requirements for PGIP physician organizations as announced at the PGIP Quarterly on Sept. 8:
- POs must have 75 or more TRUST panel physicians or Traditional participating physicians, 50 of whom must be practicing as primary care providers in internal medicine, pediatrics, family practice or general practice and have at least 12,500 attributed combined commercial PPO and Medicare Advantage PPO members.
- The board of the PGIP physician organization must be comprised of 51% or more Michigan-licensed practicing physicians who are members of the PPO TRUST or TRAD network and contribute to the PGIP Reward Pool.
- POs must have contractual authority to represent their physicians for this program and coordinate and facilitate practice improvements and program administration on behalf of the physicians.
- POs must continue to meet and comply with program standards, including Standards for Maintaining Quality Health Care, Standards for Health Information Privacy and Security, Standards for Controlling Health Care Costs, Standards for Assuring Appropriate Utilization of Health Care Services, and Standards for Assuring Reasonable Levels of Access to Health Care Services.
- POs must meet the minimum IT and analytic enablement requirements to actively and appropriately participate in our program. POs must meet the minimum requirements for the sharing of data between the PO and their practices, including a registry, data warehouse, Michigan Health Information Network connectivity and risk stratification tools.
Note: All POs will be expected to comply with the new and enhanced requirements by the Fall 2024 PGIP Snapshot in preparation for the 2025 PGIP program year.
Quality expectations
PGIP Evolution focuses not only on PO eligibility requirements and the support that POs provide to their physician members, but also on ensuring appropriate levels of clinical quality performance. As shared during the PO collaboration call on Oct. 25, Blue Cross is continuing to focus on multiple components that contribute to the high performance of PGIP physician organizations, particularly as they relate to our Clinical Quality Initiative, or CLQI, which focuses on HEDIS® and its stars metrics.
PGIP physician organizations are evaluated on their commercial PPO and Medicare Advantage PPO performance through this longstanding initiative. As part of PGIP Evolution, we’re addressing how POs are engaging and performing in CLQI. Beginning with the 2024 program year, Blue Cross will be engaging POs that have fallen into the bottom quartile of performance in four out of the past five years. We’ll work with these POs on quality improvement plans to increase their performance.
For the 2024 program year, these POs will need to:
- Submit action plans to Value Partnerships detailing efforts and planned resources to address performance issues and close gaps in care for each measure that falls below NCQA 75th percentile benchmark performance.
- Submit quarterly progress reports.
- Meet in person with Blue Cross leadership three times a year.
- Meet with an assigned mentor PGIP physician organization to address concerns and brainstorm solutions.
On an annual basis, we’ll be assessing all PGIP physician organizations to ensure no POs have multiple successive years of less-than-acceptable performance.
This information will be recirculated through PGIP communication channels as the Fall 2024 PGIP Snapshot nears. If you have questions, reach out to your field team representative or email valuepartnerships@bcbsm.com.
HEDIS®, which stands for Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set, is a registered trademark of the National Committee for Quality Assurance, or NCQA.
Reminder: Changes coming to prior authorization, case management functions for behavioral health services in January
Starting Jan. 1, 2024, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network will consolidate the prior authorization and case management functions for behavioral health services, including treatment for autism.
We recently communicated these changes in The Record and BCN Provider News.
Prior authorization and concurrent review requests will be managed through Blue Cross Behavioral Health℠ . Case management services will be handled through Blue Cross Coordinated Care℠ . These programs will align and standardize prior authorization and case management functions for members. The changes will affect most members covered by Blue Cross commercial, Medicare Plus Blue℠, BCN commercial and BCN Advantage℠ plans.
Find details in the FAQ
We updated the Blue Cross Behavioral Health: Frequently asked questions for providers document with the latest information. Here are the most recent changes:
- In the “Submitting prior authorization requests and concurrent review requests” section:
- We outlined how to submit requests electronically and by phone, before and after Jan. 1.
- We listed the medical necessity criteria we’ll use to make determinations on these requests.
- In the “Autism evaluation and treatment changes” section, we added information about:
- Additional opportunities for members to obtain a comprehensive diagnostic autism evaluation prior to starting treatment
- How to request a “bridge authorization,” which allows members to start applied behavior analysis, or ABA, treatment while they’re in the process of completing the components of the comprehensive evaluation
- In the “Appeals” section, we updated the information to show that you should follow the instructions in the determination letter to submit an appeal of a request that wasn’t approved.
You can access the FAQ at ereferrals.bcbsm.com on the:
Watch for a recorded webinar
In December, we’ll publish a recorded webinar, which will provide:
- An overview of the changes
- Instructions on how to access and use the Blue Cross Behavioral Health provider portal
- Information about where to locate important resources
- Watch for upcoming communications on how to access the webinar.
Update: We’ve added extended fees for some external peer reviews
As previously communicated in a September 2023 Record article, we recently increased the cost for external reviews. The base cost of a standard clinical review is $378 per review. The base cost of a coding review is $334.
Extended fees will apply to the scenarios listed below and billed at the base rate plus $125 each hour after.
- Documentation exceeding 2,000 pages
- Diagnoses greater than or equal to three codes
According to Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network participation agreements with health care providers, the facility or practitioner’s office is responsible for paying the total cost of the appeal review if the peer review agency upholds Blue Cross’ decision regarding a claim.
We’ll use updated 2023 InterQual criteria, starting Feb. 1
On Feb. 1, 2024, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network will start using updated 2023 InterQual® criteria to make determinations on prior authorization requests for the services we manage.
Change Healthcare published updates to its 2023 InterQual criteria on Oct. 6, 2023. Refer to the table below to see which updated criteria we’re adopting. When you open the documents linked below, you’ll see the changes in red.
How we’ll use the updated criteria
We’ll use the updated criteria to make determinations on prior authorization requests for non-behavioral health services for the following members:
- Blue Cross commercial
- Medicare Plus Blue℠
- BCN commercial
- BCN Advantage℠
When clinical information is requested for a medical or surgical admission or for other services, we require providers to submit specific components of the medical record that show that the request meets the criteria. We review this information when making determinations on prior authorization requests.
This information:
- Applies to lines of business and members whose authorizations are managed by Blue Cross or BCN directly and not by independent companies that provide services to Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan
- Doesn’t apply to behavioral health services
No updates to our local rules
We’re not updating our local rules. We use InterQual criteria and our local rules when making determinations on prior authorization requests for Blue Cross and BCN commercial members for these types of post-acute care:
- Skilled nursing
- Inpatient rehabilitation
- Long-term acute care
You can access the local rules for post-acute care as follows:
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network don’t own or control this website.
Changes to preferred drug designations and prior authorization requirements for Medicare Advantage members
For dates of service on or after Jan. 1, 2024, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network are making changes to the preferred and nonpreferred designations for some medical benefit drugs.
In addition, health care providers will need to submit prior authorization requests through different systems for some preferred and nonpreferred drugs.
These changes will affect most Medicare Plus Blue℠ members and BCN Advantage℠ members.
Preferred drug designations are changing
Starting Jan. 1, we’re changing preferred drug designations as shown in the following table.
Changes are in bold text.
Reference product |
Preferred drugs |
Before Jan. 1, 2024 |
On or after Jan. 1, 2024 |
Bevacizumab |
- Mvasi®, HCPCS code Q5107
- Zirabev®, HCPCS code Q5118
|
|
Infliximab |
- Avsola®, HCPCS code Q5121
- Inflectra®, HCPCS code Q5103
|
- Avsola, HCPCS code Q5121
- Renflexis®, HCPCS code Q5104
|
Pegfilgrastim |
- Fulphila®, HCPCS code Q5108
- Neulasta®, Neulasta® OnPro®, HCPCS code J2506
- Ziextenzo®, HCPCS code Q5120
|
- Neulasta, Neulasta OnPro, HCPCS code J2506
- Nyvepria®, HCPCS code Q5122
|
Rituximab |
- Riabni™, HCPCS code Q5123
- Ruxience®, HCPCS code Q5119
|
- Ruxience, HCPCS code Q5119
- Truxima®, HCPCS code Q5115
|
Trastuzumab |
- Kanjinti®, HCPCS code Q5117
- Trazimera®, HCPCS code Q5116
|
- Kanjinti, HCPCS code Q5117
- Ogivri®, HCPCS code Q5114
|
How to submit prior authorization requests
Submit prior authorization requests as follows:
- Preferred oncology drugs will require prior authorization through Carelon Medical Benefits Management. All other preferred drugs will require prior authorization through the NovoLogix® online tool.
- Nonpreferred drugs will require prior authorization through NovoLogix.
Note: Preferred infliximab and rituximab agents don’t require prior authorization.
Reminder: Bevacizumab agents don’t require prior authorization for use in retinal disorders.
To submit a prior authorization request, log in to our provider portal (availity.com),** click on Payer Spaces in the menu bar and then click on the BCBSM and BCN logo. Then click on the tile to access the appropriate NovoLogix tool or the Carelon ProviderPortal.
Note: If you need to request access to Availity® Essentials, follow the instructions on the Register for web tools webpage at bcbsm.com/providers.
When prior authorization is required
These drugs will require prior authorization when they’re administered by a health care provider in sites of care such as outpatient facilities or physician offices and are billed in one of the following ways:
- Electronically through an 837P transaction or on a professional CMS-1500 claim form
- Electronically through an 837I transaction or using the UB04 claim form for a hospital outpatient type of bill 013x
List of requirements
For a list of requirements related to drugs covered under the medical benefit, see the Medical Drug and Step Therapy Prior Authorization List for Medicare Plus Blue and BCN Advantage members.
We’ll update the list to reflect these changes prior to the effective date.
Availity is an independent company that contracts with Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network to offer provider portal and electronic data interchange services.
Carelon Medical Benefits Management is an independent company that contracts with Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network to manage prior authorizations for select services. For more information, go to our ereferrals.bcbsm.com website.
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network don’t own or control this website.
Blue Cross, BCN covering additional vaccines
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network want to increase access to vaccines and decrease the risk of vaccine-preventable disease outbreaks. As a result, we’ve added the following vaccine to our list of vaccines covered under the pharmacy benefit:
Vaccine |
Common name and abbreviation |
Effective date |
Beyfortus™ |
Respiratory syncytial virus — RSV |
Sept. 28, 2023 |
The following lists all the vaccines covered under eligible members’ prescription drug plans. Most Blue Cross and BCN commercial (non-Medicare) members with prescription drug coverage are eligible. If a member meets the coverage criteria, the vaccine is covered with no cost sharing.
Vaccines that have an age requirement
Vaccine |
Common name and abbreviation |
Age Requirement |
Gardasil 9® |
Human papillomavirus vaccine — HPV |
9 to 45 years old |
Influenza virus |
Influenza vaccine — flu |
Under 9: 2 vaccines per 180 days
9 and older: 1 vaccine per 180 days |
Prevnar 13® |
Pneumococcal 13 — valent conjugate vaccine |
65 and older |
Vaccines that have no age requirement
Plan |
How it works |
Dengvaxia® |
Dengue vaccine — DEN4CYD |
Daptacel®
Infanrix®
|
Diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis vaccine — DTaP |
Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoids |
Diphtheria, tetanus vaccine — DT |
Kinrix®
Quadracel®
|
DTap and inactivated poliovirus vaccine — DTaP-IPV |
Pediarix® |
DTaP, hepatitis B, and inactivated poliovirus vaccine — DTaP-HepB-IPV |
Vaxelis®
|
DTaP, inactivated poliovirus, Haemophilus influenzae type b, and hepatitis B vaccine — DTaP-IPV-Hib-HepB |
ActHIB®
Hiberix®
PedvaxHIB®
|
Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine — Hib |
Havrix®
Vaqta®
|
Hepatitis A — HepA |
Engerix-B®
Heplisav-B®
PreHevbrio™
Recombivax HB®
|
Hepatitis B — HepB |
Twinrix®
|
Hepatitis A & B — HepA-HEPB |
M-M-R II®
Priorix®
|
Measles, mumps, rubella vaccine — MMR |
ProQuad® |
Measles, mumps, rubella and varicella vaccine — MMRV |
Menveo®
|
Meningococcal serogroups A, C, W, Y vaccine — MenACWY-CRM |
Menactra® |
Meningococcal serogroups A, C, W, Y vaccine — MenACWY-D |
MenQuadfi® |
Meningococcal serogroups A, C, W, Y vaccine — MenACWY-TT |
Bexsero® |
Meningococcal serogroup B vaccine — MenB-4C |
Trumenba® |
Meningococcal serogroup B vaccine — MenB-FHbp |
Vaxneuvance™ |
Pneumococcal 15-valent conjugate vaccine — PCV15 |
Prevnar 20™ |
Pneumococcal 20-valent conjugate vaccine — PCV20 |
Pneumovax 23® |
Pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine — PPSV23 |
IPOL® |
Poliovirus — IPV |
Arexvy™
Abrysvo™
Beyfortus™
|
Respiratory syncytial virus — RSV |
Rotarix® |
Rotavirus vaccine — RV1 |
RotaTeq® |
Rotavirus vaccine — RV5 |
Tdvax®
Tenivac®
|
Tetanus and diphtheria vaccine — Td |
Adacel®
Boostrix® |
Tetanus, diphtheria and acellular pertussis vaccine — Tdap |
Varivax® |
Varicella vaccine — VAR or chickenpox |
Shingrix® |
Zoster vaccine — RZV or shingles |
COVID-19 vaccines |
- Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine (2023-24) — ages 6 months to 4 years old
- Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine (2023-24) — ages 5 to 11 years old
- Comirnaty, Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine (2023-24)
- Spikevax, Moderna COVID-19 vaccine (2023-24)
- Novavax COVID-19 vaccine (2023-24)
|
If a member doesn’t meet the age requirement for a vaccine, Blue Cross and BCN won’t cover the vaccine under the prescription drug plan, and the claim will reject.
Vaccines must be administered by certified, trained and qualified registered pharmacists.
Changes coming to infliximab step therapy requirements for Medicare Advantage members in January
For dates of service on or after Jan. 1, 2024, infliximab step therapy requirements are changing for Cimzia®, Skyrizi® IV and Ilumya®. These changes apply to Medicare Plus Blue℠ and BCN Advantage℠ members.
Notes:
- These drugs are part of members’ medical benefits, not their pharmacy benefits.
- These drugs require prior authorization. Submit requests through the NovoLogix® online tool.
Requirements added for Cimzia and Skyrizi
Starting Jan. 1, members will have to try and fail a preferred infliximab drug before a health care provider requests prior authorization for the following drugs:
- Cimzia (certolizumab pegol), HCPCS code J0717
- Skyrizi IV (risankizumab-rzaa), HCPCS code J2327
For information about preferred drug designations, see our provider alert, Update: Changes to preferred drug designations and prior authorization requirements for Medicare Advantage members.
Requirements removed for Ilumya
Starting Jan. 1, members won’t have to try and fail a preferred infliximab drug before using Ilumya.
Ilumya will continue to require prior authorization.
How to submit prior authorization requests
To submit a prior authorization request, log in to our provider portal, availity.com,** click on Payer Spaces in the menu bar and then click on the BCBSM and BCN logo. Then click on the tile to access the appropriate NovoLogix tool.
If you need to request access to Availity® Essentials, follow the instructions on the Register for web tools webpage at bcbsm.com/providers.
When prior authorization is required
The drugs mentioned above require prior authorization when they are administered by a provider in sites of care such as outpatient facilities or physician offices and are billed in one of the following ways:
- Electronically through an 837P transaction or on a professional CMS-1500 claim form
- Electronically through an 837I transaction or using the UB04 claim form for a hospital outpatient type of bill 013x
List of requirements
For a list of requirements related to drugs covered under the medical benefit, see the Medical Drug and Step Therapy Prior Authorization List for Medicare Plus Blue and BCN Advantage members.
We’ll update the list to reflect these changes prior to the effective date.
Availity® is an independent company that contracts with Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network to offer provider portal and electronic data interchange services.
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan doesn’t own or control this website.
Syfovre and Izervay must not be used with other geographic atrophy drugs for commercial members
For dates of service on or after Nov. 24, 2023, the following drugs must not be used in combination with each other or any other geographic atrophy, or GA, drug:
- Syfovre® (pegcetacoplan), HCPCS codes J3490 and C9151
- Izervay™ (avacincaptad pegol), HCPCS code J3590
This change affects Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan commercial members and Blue Care Network commercial members.
Syfovre and Izervay will continue to require prior authorization through NovoLogix®, as specified in the Blue Cross and BCN utilization management medical drug list for Blue Cross commercial and BCN commercial members.
Some Blue Cross commercial groups not subject to these requirements
For Blue Cross commercial groups, this authorization requirement applies only to groups that participate in the standard commercial Medical Drug Prior Authorization Program for drugs administered under the medical benefit. To determine whether a group participates in the prior authorization program, see the Specialty Pharmacy Prior Authorization Master Opt-in/out Group list.
Note: Blue Cross and Blue Shield Federal Employee Program® members and UAW Retiree Medical Benefits Trust (non-Medicare) members don’t participate in the standard prior authorization program.
Additional information
For additional information about drugs covered under the medical benefit, see the following pages of the ereferrals.bcbsm.com website:
Prior authorization isn’t a guarantee of payment. Health care practitioners need to verify eligibility and benefits for members.
Tecvayli will have additional requirements for most commercial members, starting Dec. 7
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network are updating the medical policy for Tecvayli® (teclistamab-cqyv), HCPCS code J9380. The requirements in the updated medical policy will apply for most Blue Cross and BCN commercial members for dates of service on or after Dec. 7, 2023.
In keeping with the updated medical policy, members will have to meet the following additional requirements for treatment with Tecvayli to be considered medically necessary:
- Alanine aminotransferase, or ALT, and aspartate aminotransferase, or AST, less than or equal to three times the upper limit of normal, or ULN
- Creatinine clearance greater than or equal to 40 mL/min
- Left ventricular ejection fraction greater than or equal to 40%
- No active autoimmune disease except vitiligo, Type 1 diabetes mellitus or prior autoimmune thyroiditis
You can see the full list of requirements in the updated medical policy, which will be available by Dec. 7. To view the policy, go to the Medical Policy Router Search page, enter the name of the drug in the Policy/Topic Keyword field and press Enter. The search results will include links to both the current medical policy and the updated medical policy.
Note: To access the Medical Policy Router Search page, go to bcbsm.com/providers, click on Resources and then click on Search Medical Policies.
Some Blue Cross commercial groups aren’t subject to these requirements
For Blue Cross commercial groups, this authorization requirement applies only to groups that participate in the standard commercial Medical Drug Prior Authorization Program for drugs administered under the medical benefit. To determine whether a group participates in the prior authorization program, see the Specialty Pharmacy Prior Authorization Master Opt-in/out Group list.
Note: Blue Cross and Blue Shield Federal Employee Program® members and UAW Retiree Medical Benefits Trust (non-Medicare) members don’t participate in the standard prior authorization program.
Additional information
For additional information about drugs covered under the medical benefit, see the following pages of the ereferrals.bcbsm.com website:
Prior authorization isn’t a guarantee of payment. Health care practitioners need to verify eligibility and benefits for members.
Vyvgart Hytrulo to have a site-of-care requirement for most commercial members, starting Jan. 1
For dates of service on or after Jan. 1, 2024, we’re adding a site-of-care requirement for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network group and individual commercial members for the following drug covered under the medical benefit:
- Vyvgart® Hytrulo (efgartigimod alfa and hyaluronidase-qvfc), HCPCS code J3590
The NovoLogix® online tool will prompt you to select a site of care when you submit prior authorization requests for this drug. If the request meets clinical criteria for the drug and is for one of the following sites of care, it will be approved automatically:
- Doctor’s or other health care provider’s office
- Ambulatory infusion center
- The member’s home, from a home infusion therapy provider
Additional information or documentation may be required for requests to administer Vyvgart Hytrulo in an outpatient hospital setting.
As a reminder, this drug already requires prior authorization; providers can submit prior authorization requests using NovoLogix®. The new site-of-care requirement is in addition to the current prior authorization requirement.
Members who start courses of treatment with Vyvgart Hytrulo before Jan. 1, 2024, will be able to continue receiving the drug in their current location until their existing authorization expires. If those members then continue treatment under a new prior authorization, the site-of-care requirement outlined above will apply.
Some Blue Cross commercial groups not subject to these requirements
For Blue Cross commercial groups, the prior authorization and site-of-care requirements apply only to groups that participate in the standard commercial Medical Drug Prior Authorization Program for drugs administered under the medical benefit. To determine whether a group participates in the prior authorization program, see the Specialty Pharmacy Prior Authorization Master Opt-in/out Group List.
Note: Blue Cross and Blue Shield Federal Employee Program® members and UAW Retiree Medical Benefits Trust (non-Medicare) members don’t participate in the standard prior authorization program.
List of requirements
For a full list of requirements related to drugs covered under the medical benefit, see the Blue Cross and BCN utilization management medical drug list for Blue Cross commercial and BCN commercial members. We’ll update this list prior to the effective date.
You can access this list and other information about requesting prior authorization at ereferrals.bcbsm.com, on these webpages:
Authorization isn't a guarantee of payment. Health care practitioners need to verify eligibility and benefits for members.
How to submit BCN, Medicare Plus Blue and BCN Advantage skin biopsy claims for payment
Procedure code *11102 is related to biopsy procedures on the skin. As of October 2023, we pay Medicare Plus Blue℠, BCN Advantage℠ and Blue Care Network claims for this procedure code if the following statements apply:
- Procedure code *11102 is reported with other integumentary codes.
- Modifier 59 and related XE, XS, XP and XU modifiers are appended on the claims.
Reminder: Health care providers should continue following the guidelines communicated in our September 2021 article. This applies to appending modifier 59 and related XE, XS, XP and XU modifiers.
We no longer automatically pay for certain procedures that are billed with modifier 59 and related XE, XS, XP and XU modifiers, when they’re billed with a procedure code on the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ National Correct Coding Initiative Procedure-to-Procedure list.
Only select codes allow modifier 59 and related XE, XS, XP and XU modifiers to automatically bypass the National Council on Compensation Insurance code-pair edits.
The additional review assures that claims have been coded correctly for more complex situations where an overriding modifier has been appended.
Providers should:
- Code claims to the level of specificity for the services rendered.
- Appropriately append diagnosis codes and modifiers following the guidelines published by the American Medical Association and CMS.
The reported services should be supported in the patient’s medical record.
Note: Claims can be resubmitted for payment.
We’ve updated our chiropractic and osteopathic manipulation benefits
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan has updated its chiropractic and osteopathic manipulation benefits to combine outpatient facility and professional member accumulation visit maximums and cost share. The updates were effective for all applicable groups for dates of service on and after Sept. 1, 2023.
These changes apply to the following Blue Cross commercial groups that have chiropractic and osteopathic benefits:
- Fully insured
- Self-funded
When an outpatient facility and professional claim is reported in Place of Service 2 (outpatient hospital) for the same encounter on the same date of service, the accumulated service counts as only one visit toward the member’s benefit maximum. If a member receives an additional manipulation on the same date in a different POS 3 (office), the visit will be accumulated as a separate visit toward the member’s visit maximum.
Professional and facility existing group cost share won’t change. Services performed in a facility setting will apply facility cost share while services in an office setting will apply an office cost share.
Revenue code 0531 was turned on to accommodate the billing and reimbursement of osteopathic manipulations when reported with a valid CPT procedure code. This revenue code will apply fee-based reimbursement for the applicable codes.
The alignment of the benefits across both an outpatient facility and a provider’s office allows Blue Cross to adapt to the growing changes in provider billing practices. The changes will ensure compliance with benefit plan designs for our groups and will consistently apply benefit experiences regardless of where services are provided.
Note: Claims will continue to deny manipulation services when a group doesn’t have chiropractic or osteopathic benefits.
We’re making chiropractic, and sleeve gastrectomy and hernia repair payment policy updates
Chiropractic: Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan is updating its payment policy to no longer apply a bundling edit when procedure code *98943 is billed with other specified chiropractic manipulative treatment codes. Procedure code *98943 will be eligible to receive separate reimbursement at 50% of the allowed amount when billed with *98940, *98941 and *98942. This update will apply to claims processed starting in January.
Sleeve gastrectomy and hernia repair: Starting in March 2024, Blue Cross will be updating its payment policy to apply bundling edits to internal hernia repair codes when billed with bariatric surgery codes. Hernia repair codes won’t receive separate reimbursement when billed with bariatric surgery codes as they are considered incidental or mutually exclusive to the bariatric procedure. The specified codes applicable to this policy are as follows:
- Internal hernia repair codes: *43280, *43281, *43282, *43283
- Bariatric surgery codes: *43770, *43771, *43772, *43773, *43774, *43775
Blue Cross increases number of procedure codes payable to podiatrists
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan is now allowing additional Current Procedural Terminology and Health Care Procedure Coding System codes to be payable to podiatrists.
We’ve made this change to align with Medicare and make it easier for podiatrists to do business with us.
Procedure codes *11400, *11401, *11402, *20606, *76882, *76942, *93922 and *93923 are within the scope of practice for a podiatrist; therefore they’re reimbursable when reported by this provider specialty.
These codes are payable based on the dates of service below:
Procedure codes |
Payable for dates of service on or after |
*11400, *11401, *11402, *20606 |
Aug. 11, 2023 |
*76882, *76942
|
May 18, 2023 |
*93922, *93923 |
June 17, 2022 |
Group-specific rules and benefits still apply. Verify your patients’ benefits for coverage.
New payability limitation in Benefit Explainer: Rendering Provider Designation
We’ve enhanced Benefit Explainer to include a new payability limitation called Rendering Provider Designation.
This new designation will first be used to indicate whether a Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan member has access to our Virtual Primary Care program, which launches Jan. 1, 2024, and what the member’s cost share would be if they choose to use the program.
Here’s a screenshot** of what Benefit Explainer users can expect to see.
**This screenshot example is for illustrative purposes and may not reflect actual data.
New resources to support staff and improve patient experience
During the past year, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan’s Patient Experience team incorporated member, doctor and physician organization feedback to shape the resources and support we provide to physician practices. Throughout 2023, we engaged with many practices and physician organizations across Michigan to improve patient interactions, access to care and care coordination.
New training for your staff
One of our newest all-staff training focuses on dealing with challenging patients. These sessions, available in person and virtually, provide strategies to remain calm and diffuse situations with upset patients and complement our Patient Communication session that offers best practices for a great patient experience.
Email PatientExperience@bcbsm.com for more information or to schedule a session.
Webinars on demand
Visit the on-demand page of our Patient Experience site for webinars and training. These sessions are created to fit into your schedule and can be accessed at any time. Current offerings include:
- Combatting Burnout in the Health Care Setting is a five-part series that helps health care workers manage stress and burnout by providing practical strategies to maintain their own well-being.
- A three-part series that focuses on the CG-CAHPS Care domains — Getting Care Quickly, Care Coordination and Getting Needed Care — provides tips to improve processes such as medication reconciliation, lab and other test result follow-up, managing in-office wait times, specialist referrals and getting routine appointments quickly.
See the Additional Resources page for more training opportunities.
Specialist referral tactic
Earlier this year, Blue Cross’ Patient Experience team released its specialist referral folder, a new tactic to help practices manage patient expectations when referred to specialists. The folder helps guide the conversation about the time it may take to get an appointment with common specialists, definitions, a spot for medication lists and the specialist’s contact information. Paperwork pertinent to the referral can be kept in the folder so everything the patient needs for a successful appointment is in one place.
Patient Experience resources include a variety of tactic materials that center around the CAHPS Care domains. Materials include handouts, signs, and other tools for patients and staff.
We’re updating our site to enable visitors to view tactic materials, including the specialist referral folder and many other materials, such as tactics to improve wait times, medication reconciliation, patient portal use and more. Check out the Patient Experience site for more information.
Coming soon
Visit our Patient Experience site to discover new content and register for upcoming webinars, including sessions on telehealth interactions and health equity.
For information or to request a patient experience consultation, email PatientExperience@bcbsm.com.
Lunch and learn webinars for physicians and coders focus on risk adjustment, coding
As a reminder, we’re offering live, 30-minute educational webinars that provide updated information on documentation and coding for common challenging diagnoses. Webinars include an opportunity to ask questions.
Here’s our upcoming webinar schedule and topic tentatively scheduled. The session starts at noon Eastern time. Log in to the provider training website to register.
Session date |
Topic |
Dec. 13 |
CPT coding scenarios for 2024 |
To access the training site, follow these steps:
- Log in to the provider portal
- Click on Payer Spaces on the menu bar and then click on the BCBSM and BCN logo.
- Under Applications, click on the Provider Training Site tile
- Click on Submit on the Select an Organization page
- Existing users who used the same email address as their provider portal profile email will be directed to the training site. If you used a different email address, contact ProviderTraining@bcbsm.com to update your profile.
Note: If you’re a new training site user, complete the one-time registration by entering your role and creating a password. This allows you to access the training site outside of the provider portal if needed.
If you need assistance navigating the provider training site, email ProviderTraining@bcbsm.com.
Locating a session
Click here to log in if you’re already registered for the provider training website. On the provider training website, look in the Event Calendar or use the search feature with the keyword “lunch” to quickly locate the 2023 sessions.
See the screenshots below for more details.
Previous sessions
You can also listen to previously recorded sessions. Check out the following:
Date |
Topic |
April 26 |
HCC and risk adjustment coding scenarios |
May 17 |
Coding neoplasms |
June 21 |
Coding diabetes and hypertension |
July 19 |
Coding heart disease and vascular disease |
Aug. 16 |
Medical Record Documentation and MEAT |
Sept. 20 |
Coding Tips for COPD and asthma |
Oct. 18 |
ICD-10-CM updates and changes for 2024 |
Nov. 15 |
Coding kidney disease and rheumatoid arthritis |
For more information
If you have any questions about the sessions, contact April Boyce at aboyce@bcbsm.com. If you have questions regarding a session or website registration, email ProviderTraining@bcbsm.com.
We’ve updated questionnaires in e-referral system
On Oct. 15, 2023, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network updated questionnaires in the e-referral system. We’ve also updated the corresponding preview questionnaires on the ereferrals.bcbsm.com website.
As a reminder, we use our authorization criteria, our medical policies and your answers to the questionnaires in the e-referral system when making utilization management determinations on your prior authorization requests.
Updated questionnaires
We’ve updated the following questionnaires in the e-referral system:
Questionnaire |
Opens for |
Details |
Left atrial appendage closure |
BCN commercial |
Updated a question |
Thyroidectomy, partial |
- Medicare Plus Blue℠
- BCN commercial
- BCN Advantage℠
|
- Updated three questions
- Added a question
|
Preview questionnaires
Preview questionnaires show the questions you’ll need to answer in the e-referral system so you can prepare your answers ahead of time.
To find the preview questionnaires, go to ereferrals.bcbsm.com:
- For Medicare Plus Blue: Click on Blue Cross and then click on Authorization Requirements & Criteria. Scroll down and look under the Authorization criteria and preview questionnaires – Medicare Plus Blue heading.
- For BCN: Click on BCN and then click on Authorization Requirements & Criteria. Scroll down and look under the Authorization criteria and preview questionnaires heading.
Authorization criteria and medical policies
The Authorization Requirements & Criteria pages explain how to access the pertinent authorization criteria and medical policies.

Reminder: Changes coming to prior authorization, case management functions for behavioral health services in January
Starting Jan. 1, 2024, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network will consolidate the prior authorization and case management functions for behavioral health services, including treatment for autism.
We recently communicated these changes in The Record and BCN Provider News.
Prior authorization and concurrent review requests will be managed through Blue Cross Behavioral Health℠ . Case management services will be handled through Blue Cross Coordinated Care℠ . These programs will align and standardize prior authorization and case management functions for members. The changes will affect most members covered by Blue Cross commercial, Medicare Plus Blue℠, BCN commercial and BCN Advantage℠ plans.
Find details in the FAQ
We updated the Blue Cross Behavioral Health: Frequently asked questions for providers document with the latest information. Here are the most recent changes:
- In the “Submitting prior authorization requests and concurrent review requests” section:
- We outlined how to submit requests electronically and by phone, before and after Jan. 1.
- We listed the medical necessity criteria we’ll use to make determinations on these requests.
- In the “Autism evaluation and treatment changes” section, we added information about:
- Additional opportunities for members to obtain a comprehensive diagnostic autism evaluation prior to starting treatment
- How to request a “bridge authorization,” which allows members to start applied behavior analysis, or ABA, treatment while they’re in the process of completing the components of the comprehensive evaluation
- In the “Appeals” section, we updated the information to show that you should follow the instructions in the determination letter to submit an appeal of a request that wasn’t approved.
You can access the FAQ at ereferrals.bcbsm.com on the:
Watch for a recorded webinar
In December, we’ll publish a recorded webinar, which will provide:
- An overview of the changes
- Instructions on how to access and use the Blue Cross Behavioral Health provider portal
- Information about where to locate important resources
- Watch for upcoming communications on how to access the webinar.
For commercial LTACH requests, questionnaire opens in e-referral system
When submitting a prior authorization request for an admission to a long-term acute care hospital, or LTACH, you must complete a questionnaire about the three skilled nursing facilities, or SNFs, you have contacted.
These must be SNFs you believe may be able to provide care for the member but that have indicated they can’t provide the level of care the member requires.
This applies to LTACH placement requests for most Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network commercial members.
You must provide the following information:
- Whether you’ve contacted three SNFs (yes or no)
- Name and contact information for each SNF
Follow the prompts in the questionnaire to ensure you’ve provided the information that’s required.
If the required information isn’t included when you submit the prior authorization request, the request is considered incomplete and can’t be processed. We’ll reach out to you and ask that you resubmit the request when the information is available. This delays the processing of the request.
Be aware that:
- The three SNFs must be contracted with Blue Cross or BCN and located within 75 miles of the facility in which the member is currently a patient.
- Two of the three SNFs must be facilities that can accommodate members who need higher levels of care such as complex wound care or total parenteral nutrition.
You can read more about these and other requirements in the document Blue Cross and BCN Local Rules for 2023 for post-acute care: Modifications of InterQual® criteria.
You can access this document at ereferrals.bcbsm.com, on these webpages:
Blue Cross updating reimbursement policy for administering blood transfusions at inpatient facilities
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network will no longer reimburse separate claims for administering blood transfusions at inpatient facilities, effective Feb. 1, 2024.
This policy applies to all inpatient facility claims submitted for Blue Cross and BCN commercial members.
A blood transfusion is a routine medical procedure generally administered by nursing staff. Nursing services should be included in the general cost of the room where services are being given; therefore this service is considered ineligible for separate reimbursement.
When billing blood administration on a UB-04 for inpatient services, use the correct revenue code 0391.
Additional information
A blood transfusion is prescribed by a physician or a nonphysician practitioner for many reasons, including, but not limited to, surgery, injury and bleeding disorders.
Our updated reimbursement policy isn’t intended to affect decision-making for patient care, and health care providers are expected to apply medical judgment when caring for all members.
Benefit Explainer has new payability limitation for Primary or Secondary Diagnosis
On Nov. 20, 2023, we added Primary or Secondary Diagnosis as a new payability limitation to Benefit Explainer. When users view standalone Primary or Secondary Diagnosis, Primary Diagnosis or Any Diagnosis rules, the information bubble icon they see will read Applies or Does not apply.
When users hover over the icon, they’ll see how the different rules apply to an outpatient facility claim billed with the same HCPCS code. When the bubble reads Applies it means the following for each rule:
Standalone Primary Diagnosis – The diagnosis restriction on the outpatient facility claim will only be based on the primary diagnosis code billed.
Standalone Primary or Secondary Diagnosis – The diagnosis restriction on the outpatient facility claim will be based on the primary diagnosis or the second diagnosis code billed.
Standalone Any Diagnosis – The diagnosis restriction on the outpatient facility claim will be based on any diagnosis code billed.
When the icon reads Does not apply for any of the above standalone diagnosis limitations, a diagnosis restriction won’t be applied to the outpatient facility claim.
Below is an example of what users will see. The example is for procedure code J0185 on the Medical/Payment Policy tab under Coverage Limitations, Medical, Primary Diagnosis.
When a user hovers over the icon, information on the diagnosis type appears.
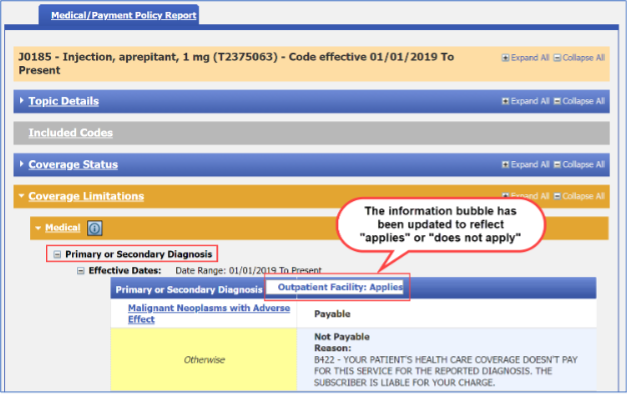
Background
Facility outpatient claims are required to be billed with a HCPCS code. During claims processing, the Medical Policy Primary Diagnosis rule for the HCPCS code is applied to the outpatient facility claim. Health care providers can submit up to 25 diagnoses on a facility claim.
The information in the icon defines the location of the diagnosis on the facility claim that should be read to apply the Medical Policy Diagnosis rule.
Note: Screenshot examples are for illustrative purposes and may not reflect actual data.
Update: We’ve added extended fees for some external peer reviews
As previously communicated in a September 2023 Record article, we recently increased the cost for external reviews. The base cost of a standard clinical review is $378 per review. The base cost of a coding review is $334.
Extended fees will apply to the scenarios listed below and billed at the base rate plus $125 each hour after.
- Documentation exceeding 2,000 pages
- Diagnoses greater than or equal to three codes
According to Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network participation agreements with health care providers, the facility or practitioner’s office is responsible for paying the total cost of the appeal review if the peer review agency upholds Blue Cross’ decision regarding a claim.
We’ll use updated 2023 InterQual criteria, starting Feb. 1
On Feb. 1, 2024, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network will start using updated 2023 InterQual® criteria to make determinations on prior authorization requests for the services we manage.
Change Healthcare published updates to its 2023 InterQual criteria on Oct. 6, 2023. Refer to the table below to see which updated criteria we’re adopting. When you open the documents linked below, you’ll see the changes in red.
How we’ll use the updated criteria
We’ll use the updated criteria to make determinations on prior authorization requests for non-behavioral health services for the following members:
- Blue Cross commercial
- Medicare Plus Blue℠
- BCN commercial
- BCN Advantage℠
When clinical information is requested for a medical or surgical admission or for other services, we require providers to submit specific components of the medical record that show that the request meets the criteria. We review this information when making determinations on prior authorization requests.
This information:
- Applies to lines of business and members whose authorizations are managed by Blue Cross or BCN directly and not by independent companies that provide services to Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan
- Doesn’t apply to behavioral health services
No updates to our local rules
We’re not updating our local rules. We use InterQual criteria and our local rules when making determinations on prior authorization requests for Blue Cross and BCN commercial members for these types of post-acute care:
- Skilled nursing
- Inpatient rehabilitation
- Long-term acute care
You can access the local rules for post-acute care as follows:
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network don’t own or control this website.
Changes to preferred drug designations and prior authorization requirements for Medicare Advantage members
For dates of service on or after Jan. 1, 2024, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network are making changes to the preferred and nonpreferred designations for some medical benefit drugs.
In addition, health care providers will need to submit prior authorization requests through different systems for some preferred and nonpreferred drugs.
These changes will affect most Medicare Plus Blue℠ members and BCN Advantage℠ members.
Preferred drug designations are changing
Starting Jan. 1, we’re changing preferred drug designations as shown in the following table.
Changes are in bold text.
Reference product |
Preferred drugs |
Before Jan. 1, 2024 |
On or after Jan. 1, 2024 |
Bevacizumab |
- Mvasi®, HCPCS code Q5107
- Zirabev®, HCPCS code Q5118
|
|
Infliximab |
- Avsola®, HCPCS code Q5121
- Inflectra®, HCPCS code Q5103
|
- Avsola, HCPCS code Q5121
- Renflexis®, HCPCS code Q5104
|
Pegfilgrastim |
- Fulphila®, HCPCS code Q5108
- Neulasta®, Neulasta® OnPro®, HCPCS code J2506
- Ziextenzo®, HCPCS code Q5120
|
- Neulasta, Neulasta OnPro, HCPCS code J2506
- Nyvepria®, HCPCS code Q5122
|
Rituximab |
- Riabni™, HCPCS code Q5123
- Ruxience®, HCPCS code Q5119
|
- Ruxience, HCPCS code Q5119
- Truxima®, HCPCS code Q5115
|
Trastuzumab |
- Kanjinti®, HCPCS code Q5117
- Trazimera®, HCPCS code Q5116
|
- Kanjinti, HCPCS code Q5117
- Ogivri®, HCPCS code Q5114
|
How to submit prior authorization requests
Submit prior authorization requests as follows:
- Preferred oncology drugs will require prior authorization through Carelon Medical Benefits Management. All other preferred drugs will require prior authorization through the NovoLogix® online tool.
- Nonpreferred drugs will require prior authorization through NovoLogix.
Note: Preferred infliximab and rituximab agents don’t require prior authorization.
Reminder: Bevacizumab agents don’t require prior authorization for use in retinal disorders.
To submit a prior authorization request, log in to our provider portal (availity.com),** click on Payer Spaces in the menu bar and then click on the BCBSM and BCN logo. Then click on the tile to access the appropriate NovoLogix tool or the Carelon ProviderPortal.
Note: If you need to request access to Availity® Essentials, follow the instructions on the Register for web tools webpage at bcbsm.com/providers.
When prior authorization is required
These drugs will require prior authorization when they’re administered by a health care provider in sites of care such as outpatient facilities or physician offices and are billed in one of the following ways:
- Electronically through an 837P transaction or on a professional CMS-1500 claim form
- Electronically through an 837I transaction or using the UB04 claim form for a hospital outpatient type of bill 013x
List of requirements
For a list of requirements related to drugs covered under the medical benefit, see the Medical Drug and Step Therapy Prior Authorization List for Medicare Plus Blue and BCN Advantage members.
We’ll update the list to reflect these changes prior to the effective date.
Availity is an independent company that contracts with Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network to offer provider portal and electronic data interchange services.
Carelon Medical Benefits Management is an independent company that contracts with Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network to manage prior authorizations for select services. For more information, go to our ereferrals.bcbsm.com website.
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network don’t own or control this website.
Changes coming to infliximab step therapy requirements for Medicare Advantage members in January
For dates of service on or after Jan. 1, 2024, infliximab step therapy requirements are changing for Cimzia®, Skyrizi® IV and Ilumya®. These changes apply to Medicare Plus Blue℠ and BCN Advantage℠ members.
Notes:
- These drugs are part of members’ medical benefits, not their pharmacy benefits.
- These drugs require prior authorization. Submit requests through the NovoLogix® online tool.
Requirements added for Cimzia and Skyrizi
Starting Jan. 1, members will have to try and fail a preferred infliximab drug before a health care provider requests prior authorization for the following drugs:
- Cimzia (certolizumab pegol), HCPCS code J0717
- Skyrizi IV (risankizumab-rzaa), HCPCS code J2327
For information about preferred drug designations, see our provider alert, Update: Changes to preferred drug designations and prior authorization requirements for Medicare Advantage members.
Requirements removed for Ilumya
Starting Jan. 1, members won’t have to try and fail a preferred infliximab drug before using Ilumya.
Ilumya will continue to require prior authorization.
How to submit prior authorization requests
To submit a prior authorization request, log in to our provider portal, availity.com,** click on Payer Spaces in the menu bar and then click on the BCBSM and BCN logo. Then click on the tile to access the appropriate NovoLogix tool.
If you need to request access to Availity® Essentials, follow the instructions on the Register for web tools webpage at bcbsm.com/providers.
When prior authorization is required
The drugs mentioned above require prior authorization when they are administered by a provider in sites of care such as outpatient facilities or physician offices and are billed in one of the following ways:
- Electronically through an 837P transaction or on a professional CMS-1500 claim form
- Electronically through an 837I transaction or using the UB04 claim form for a hospital outpatient type of bill 013x
List of requirements
For a list of requirements related to drugs covered under the medical benefit, see the Medical Drug and Step Therapy Prior Authorization List for Medicare Plus Blue and BCN Advantage members.
We’ll update the list to reflect these changes prior to the effective date.
Availity® is an independent company that contracts with Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network to offer provider portal and electronic data interchange services.
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan doesn’t own or control this website.
Syfovre and Izervay must not be used with other geographic atrophy drugs for commercial members
For dates of service on or after Nov. 24, 2023, the following drugs must not be used in combination with each other or any other geographic atrophy, or GA, drug:
- Syfovre® (pegcetacoplan), HCPCS codes J3490 and C9151
- Izervay™ (avacincaptad pegol), HCPCS code J3590
This change affects Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan commercial members and Blue Care Network commercial members.
Syfovre and Izervay will continue to require prior authorization through NovoLogix®, as specified in the Blue Cross and BCN utilization management medical drug list for Blue Cross commercial and BCN commercial members.
Some Blue Cross commercial groups not subject to these requirements
For Blue Cross commercial groups, this authorization requirement applies only to groups that participate in the standard commercial Medical Drug Prior Authorization Program for drugs administered under the medical benefit. To determine whether a group participates in the prior authorization program, see the Specialty Pharmacy Prior Authorization Master Opt-in/out Group list.
Note: Blue Cross and Blue Shield Federal Employee Program® members and UAW Retiree Medical Benefits Trust (non-Medicare) members don’t participate in the standard prior authorization program.
Additional information
For additional information about drugs covered under the medical benefit, see the following pages of the ereferrals.bcbsm.com website:
Prior authorization isn’t a guarantee of payment. Health care practitioners need to verify eligibility and benefits for members.
Tecvayli will have additional requirements for most commercial members, starting Dec. 7
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network are updating the medical policy for Tecvayli® (teclistamab-cqyv), HCPCS code J9380. The requirements in the updated medical policy will apply for most Blue Cross and BCN commercial members for dates of service on or after Dec. 7, 2023.
In keeping with the updated medical policy, members will have to meet the following additional requirements for treatment with Tecvayli to be considered medically necessary:
- Alanine aminotransferase, or ALT, and aspartate aminotransferase, or AST, less than or equal to three times the upper limit of normal, or ULN
- Creatinine clearance greater than or equal to 40 mL/min
- Left ventricular ejection fraction greater than or equal to 40%
- No active autoimmune disease except vitiligo, Type 1 diabetes mellitus or prior autoimmune thyroiditis
You can see the full list of requirements in the updated medical policy, which will be available by Dec. 7. To view the policy, go to the Medical Policy Router Search page, enter the name of the drug in the Policy/Topic Keyword field and press Enter. The search results will include links to both the current medical policy and the updated medical policy.
Note: To access the Medical Policy Router Search page, go to bcbsm.com/providers, click on Resources and then click on Search Medical Policies.
Some Blue Cross commercial groups aren’t subject to these requirements
For Blue Cross commercial groups, this authorization requirement applies only to groups that participate in the standard commercial Medical Drug Prior Authorization Program for drugs administered under the medical benefit. To determine whether a group participates in the prior authorization program, see the Specialty Pharmacy Prior Authorization Master Opt-in/out Group list.
Note: Blue Cross and Blue Shield Federal Employee Program® members and UAW Retiree Medical Benefits Trust (non-Medicare) members don’t participate in the standard prior authorization program.
Additional information
For additional information about drugs covered under the medical benefit, see the following pages of the ereferrals.bcbsm.com website:
Prior authorization isn’t a guarantee of payment. Health care practitioners need to verify eligibility and benefits for members.
Vyvgart Hytrulo to have a site-of-care requirement for most commercial members, starting Jan. 1
For dates of service on or after Jan. 1, 2024, we’re adding a site-of-care requirement for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network group and individual commercial members for the following drug covered under the medical benefit:
- Vyvgart® Hytrulo (efgartigimod alfa and hyaluronidase-qvfc), HCPCS code J3590
The NovoLogix® online tool will prompt you to select a site of care when you submit prior authorization requests for this drug. If the request meets clinical criteria for the drug and is for one of the following sites of care, it will be approved automatically:
- Doctor’s or other health care provider’s office
- Ambulatory infusion center
- The member’s home, from a home infusion therapy provider
Additional information or documentation may be required for requests to administer Vyvgart Hytrulo in an outpatient hospital setting.
As a reminder, this drug already requires prior authorization; providers can submit prior authorization requests using NovoLogix®. The new site-of-care requirement is in addition to the current prior authorization requirement.
Members who start courses of treatment with Vyvgart Hytrulo before Jan. 1, 2024, will be able to continue receiving the drug in their current location until their existing authorization expires. If those members then continue treatment under a new prior authorization, the site-of-care requirement outlined above will apply.
Some Blue Cross commercial groups not subject to these requirements
For Blue Cross commercial groups, the prior authorization and site-of-care requirements apply only to groups that participate in the standard commercial Medical Drug Prior Authorization Program for drugs administered under the medical benefit. To determine whether a group participates in the prior authorization program, see the Specialty Pharmacy Prior Authorization Master Opt-in/out Group List.
Note: Blue Cross and Blue Shield Federal Employee Program® members and UAW Retiree Medical Benefits Trust (non-Medicare) members don’t participate in the standard prior authorization program.
List of requirements
For a full list of requirements related to drugs covered under the medical benefit, see the Blue Cross and BCN utilization management medical drug list for Blue Cross commercial and BCN commercial members. We’ll update this list prior to the effective date.
You can access this list and other information about requesting prior authorization at ereferrals.bcbsm.com, on these webpages:
Authorization isn't a guarantee of payment. Health care practitioners need to verify eligibility and benefits for members.
We’ve updated our chiropractic and osteopathic manipulation benefits
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan has updated its chiropractic and osteopathic manipulation benefits to combine outpatient facility and professional member accumulation visit maximums and cost share. The updates were effective for all applicable groups for dates of service on and after Sept. 1, 2023.
These changes apply to the following Blue Cross commercial groups that have chiropractic and osteopathic benefits:
- Fully insured
- Self-funded
When an outpatient facility and professional claim is reported in Place of Service 2 (outpatient hospital) for the same encounter on the same date of service, the accumulated service counts as only one visit toward the member’s benefit maximum. If a member receives an additional manipulation on the same date in a different POS 3 (office), the visit will be accumulated as a separate visit toward the member’s visit maximum.
Professional and facility existing group cost share won’t change. Services performed in a facility setting will apply facility cost share while services in an office setting will apply an office cost share.
Revenue code 0531 was turned on to accommodate the billing and reimbursement of osteopathic manipulations when reported with a valid CPT procedure code. This revenue code will apply fee-based reimbursement for the applicable codes.
The alignment of the benefits across both an outpatient facility and a provider’s office allows Blue Cross to adapt to the growing changes in provider billing practices. The changes will ensure compliance with benefit plan designs for our groups and will consistently apply benefit experiences regardless of where services are provided.
Note: Claims will continue to deny manipulation services when a group doesn’t have chiropractic or osteopathic benefits.
New resources to support staff and improve patient experience
During the past year, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan’s Patient Experience team incorporated member, doctor and physician organization feedback to shape the resources and support we provide to physician practices. Throughout 2023, we engaged with many practices and physician organizations across Michigan to improve patient interactions, access to care and care coordination.
New training for your staff
One of our newest all-staff training focuses on dealing with challenging patients. These sessions, available in person and virtually, provide strategies to remain calm and diffuse situations with upset patients and complement our Patient Communication session that offers best practices for a great patient experience.
Email PatientExperience@bcbsm.com for more information or to schedule a session.
Webinars on demand
Visit the on-demand page of our Patient Experience site for webinars and training. These sessions are created to fit into your schedule and can be accessed at any time. Current offerings include:
- Combatting Burnout in the Health Care Setting is a five-part series that helps health care workers manage stress and burnout by providing practical strategies to maintain their own well-being.
- A three-part series that focuses on the CG-CAHPS Care domains — Getting Care Quickly, Care Coordination and Getting Needed Care — provides tips to improve processes such as medication reconciliation, lab and other test result follow-up, managing in-office wait times, specialist referrals and getting routine appointments quickly.
See the Additional Resources page for more training opportunities.
Specialist referral tactic
Earlier this year, Blue Cross’ Patient Experience team released its specialist referral folder, a new tactic to help practices manage patient expectations when referred to specialists. The folder helps guide the conversation about the time it may take to get an appointment with common specialists, definitions, a spot for medication lists and the specialist’s contact information. Paperwork pertinent to the referral can be kept in the folder so everything the patient needs for a successful appointment is in one place.
Patient Experience resources include a variety of tactic materials that center around the CAHPS Care domains. Materials include handouts, signs, and other tools for patients and staff.
We’re updating our site to enable visitors to view tactic materials, including the specialist referral folder and many other materials, such as tactics to improve wait times, medication reconciliation, patient portal use and more. Check out the Patient Experience site for more information.
Coming soon
Visit our Patient Experience site to discover new content and register for upcoming webinars, including sessions on telehealth interactions and health equity.
For information or to request a patient experience consultation, email PatientExperience@bcbsm.com.
Lunch and learn webinars for physicians and coders focus on risk adjustment, coding
As a reminder, we’re offering live, 30-minute educational webinars that provide updated information on documentation and coding for common challenging diagnoses. Webinars include an opportunity to ask questions.
Here’s our upcoming webinar schedule and topic tentatively scheduled. The session starts at noon Eastern time. Log in to the provider training website to register.
Session date |
Topic |
Dec. 13 |
CPT coding scenarios for 2024 |
To access the training site, follow these steps:
- Log in to the provider portal
- Click on Payer Spaces on the menu bar and then click on the BCBSM and BCN logo.
- Under Applications, click on the Provider Training Site tile
- Click on Submit on the Select an Organization page
- Existing users who used the same email address as their provider portal profile email will be directed to the training site. If you used a different email address, contact ProviderTraining@bcbsm.com to update your profile.
Note: If you’re a new training site user, complete the one-time registration by entering your role and creating a password. This allows you to access the training site outside of the provider portal if needed.
If you need assistance navigating the provider training site, email ProviderTraining@bcbsm.com.
Locating a session
Click here to log in if you’re already registered for the provider training website. On the provider training website, look in the Event Calendar or use the search feature with the keyword “lunch” to quickly locate the 2023 sessions.
See the screenshots below for more details.


Previous sessions
You can also listen to previously recorded sessions. Check out the following:
Date |
Topic |
April 26 |
HCC and risk adjustment coding scenarios |
May 17 |
Coding neoplasms |
June 21 |
Coding diabetes and hypertension |
July 19 |
Coding heart disease and vascular disease |
Aug. 16 |
Medical Record Documentation and MEAT |
Sept. 20 |
Coding Tips for COPD and asthma |
Oct. 18 |
ICD-10-CM updates and changes for 2024 |
Nov. 15 |
Coding kidney disease and rheumatoid arthritis |
For more information
If you have any questions about the sessions, contact April Boyce at aboyce@bcbsm.com. If you have questions regarding a session or website registration, email ProviderTraining@bcbsm.com.

Bypass manual review requirement for medically necessary insulin pumps
What you need to know
- Append KX and TW modifiers to avoid manual review for insulin pumps.
- Specific criteria apply and must be documented in the patient’s medical record.
- Supplier-produced records aren’t considered part of the medical record.
As stated in a May 2020 Record article, health care providers must append the KX and TW modifiers to avoid the manual review process for a medically necessary replacement insulin pump.
To avoid the manual review process, all the following must apply:
- Insulin pump malfunctioned.
- Manufacturer’s warranty has expired.
- Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan’s five-year reasonable useful lifetime, or RUL, hasn’t been reached.
- The above criteria are clearly documented in the beneficiary’s medical record.
By appending the KX and TW modifiers, you are certifying that the member’s insulin pump has malfunctioned after the manufacturer’s warranty period, but before the five-year RUL, and that the member meets Blue Cross medical criteria for an insulin pump. The KX or TW modifier can only be added to the claim if the malfunction is documented in the patient’s medical record.
As a reminder, the medical record isn’t limited to the treating practitioner’s office records, but may include records from hospitals, nursing facilities, home health agencies or other health care professionals. Records from suppliers or health care professionals with a financial interest in the claim outcome aren’t considered sufficient by themselves to determine that an item is reasonable and necessary.
Durable medical equipment prosthetic and orthotic suppliers are reminded that:
- Supplier-produced records, even if signed by the treating practitioner, and attestation letters (for example, letters of medical necessity) aren’t considered to be part of a medical record for Medicare payment purposes.
- Templates and forms, including Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services certificates of medical necessity with a date of service before Jan. 1, 2023, must be corroborated with information in the medical record.
- A prescription isn’t considered to be part of the medical record. Medical information intended to demonstrate compliance with coverage criteria may be included on the prescription but must be corroborated by information in the medical record.
- The beneficiary’s medical record must contain sufficient documentation of his or her medical condition to substantiate the necessity for the type and quantity of items ordered and for the frequency of use or replacement (if applicable). The information should include the beneficiary’s diagnosis and other pertinent information including, but not limited to, duration of the beneficiary’s condition, clinical course (worsening or improvement), prognosis, nature and extent of functional limitations, other therapeutic interventions and results, and past experience with related items.
|






