|
October 2020

Blue Cross offers incentives and training to expand use of Collaborative Care Model
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan is expanding its use of the Collaborative Care Model, a method of integrating behavioral health within a primary care setting, with participating practices. This national model** is designed to better meet the needs of patients who have behavioral health conditions, such as anxiety and depression.
Our Physician Group Incentive Program has developed an incentive structure for learning about and using the model. PGIP has joined forces with Michigan Medicine and the Michigan Center for Clinical Systems Improvement to provide training, support and technical assistance to specific practices. Training began in August 2020 and offers a tailored approach to implementing and sustaining CoCM services.
Currently, physician organizations select practices designated as Patient-Centered Medical Homes to implement this model, focusing on those that participate in Value Partnerships’ Provider-Delivered Care Management program. These practices are likely to have some of the infrastructure in place to allow them to implement the model more easily. Practices will begin implementing the model as they complete their training.
With CoCM, primary care physicians work closely with a consulting psychiatrist and a behavioral health care manager to address behavioral health issues. The psychiatrist and the behavioral health care manager meet weekly to review the cases of patients with mental health or substance use issues that have been identified in the primary care physician’s office. The care manager then brings any recommendations to the PCP, who makes the ultimate decision on whether to change the patient’s treatment. This cycle repeats until the patient’s behavioral health diagnosis is managed.
As we announced in the May Record, Blue Cross has been reimbursing medical practices for collaborative care codes and interventions, and recently eliminated member cost share for collaborative care services. These changes apply to Blue Cross’ commercial, Blue Care Network commercial, BCN Advantage℠ and Medicare Plus Blue℠ members. The overarching goal is to expand access and improve the quality of care for our members.
“Blue Cross is a leader in implementing this type of model and moving it into the commercial space,” said William Beecroft, M.D., medical director of behavioral health for Blue Cross and BCN. “Collaborative care is designed to increase behavioral health access, improve outcomes and alleviate provider burnout. Our goal is to become the national leader in the area of behavioral health, helping to make it more accessible and affordable while removing mental health stigmas.”
CoCM can also help reduce health care costs through better management of chronic conditions, reduced inpatient admissions or emergency department visits and improved medication management. A study** reported in JAMA Network Open last year confirmed that patients with a chronic disease and a mental health disorder cost twice as much as those without a mental health disorder.
Research has also shown that collaborative care provides significantly better outcomes for depression and anxiety than routine care, according to the University of Washington AIMS Center.**
While the model has been in use by early adopters at Blue Cross since 2017, a limited number of practices have implemented it as Blue Cross and its participating practices continue to develop the infrastructure and resources to support the model. We hope to implement the model in 50 new practices by the end of 2020 and will continue training, support and technical assistance through 2023.
Practices that are interested in learning more about the training and incentive opportunities available to them are encouraged to contact their physician organizations.
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan doesn’t own or control this website.
Blue HPN debuts in Michigan, nationally starting in January
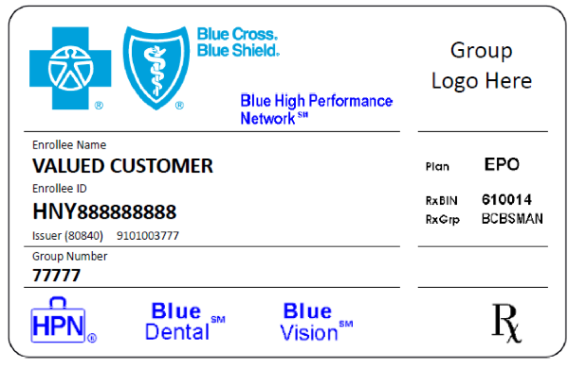
Beginning in January 2021, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan will offer a new health care plan to some groups called Blue High Performance Network℠, or Blue HPN℠. These plans feature a new network of health care providers created in partnership with doctors and hospitals in communities in Michigan and across the country. They’re designed to help deliver patient-centric care and control costs for our members and customers.
Members in these plans can see any health care provider in the Blue HPN and they will have a standard set of out-of-pocket expenses. However, if the member sees a health care provider who isn’t part of the network, they’ll be responsible for the costs (except for emergency services and urgent care).
We’ll be reaching out to enrolled members to let them know that they should see Blue HPN health care providers if they need services. You’ll know that a member has selected the Blue HPN plan by their Blue Cross ID card or in web-DENIS when you check eligibility. A sample card is included below.
We’ll have more details and information in upcoming issues of The Record, so be sure to check back often.
Blue Cross receives HITRUST CSF Certification
 We are pleased to announce that Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan has received HITRUST CSF® Certification. We are pleased to announce that Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan has received HITRUST CSF® Certification.
At Blue Cross, one of our top priorities has always been to enhance our information security capabilities. As part of that commitment, Blue Cross and Blue Care Network worked for more than two years to obtain the HITRUST CSF Certification.**
This certification recognizes our steps to continue to align with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, while ensuring we have the right level of controls and safeguards to protect sensitive patient data and reduce complexity, risk and cost. This helps minimize any negative effects on our providers, customers and organization.
HITRUST is an organization that’s responsible for creating and maintaining a comprehensive and flexible framework of prescriptive and scalable security controls in the health care sector, among others. HITRUST CSF Certification is frequently required by organizations that handle sensitive data, including protected health information, or PHI.
As part of Blue Cross’ focus on information security, we’ve developed a robust security framework that documents our policies, procedures and processes. Our framework guides how information is managed in our business to lower risk and vulnerability, and to increase confidence in an industry that increasingly uses technology to stay connected to patients. With our HITRUST CSF Certification, which attests to our information security efforts, we’ll continue to make improvements in how we protect sensitive information and manage information and compliance.
Threats to information security
The threats facing the health care industry are becoming increasingly sophisticated, with the average cost of a data breach to an organization amounting to $3.92 million, according to IBM Security. Fraudulent individuals use several social engineering techniques, such as phishing and physical breaches to obtain PHI, such as medical records, Social Security information and insurance accounts. Medical records are considered one of the most valuable type of consumer data in the world, second only to intellectual property and state secrets.
This value stems primarily from two unique features:
- Durability. Medical records are permanent — a consumer can’t merely “cancel” a health care record the way they can petition the bankruptcy court to eliminate debt.
- Ease of monetization. Medical records can quickly be monetized in many ways — through Medicare fraud, medical identity theft, illegal prescription drug resale, and any number of black market exchanges.
Our commitment to you
Our HITRUST journey underscored the importance of information security in the face of increased threats to the health care industry. But this is only the beginning.
As part of our network of physicians and other medical partners, you can expect to see:
- Continued commitment to taking every measure available to protect and secure patient — and member — PHI
- Diligence in detecting and rapidly responding to cybersecurity events or incidents
- Recertifying with HITRUST in the future to keep Blue Cross up to date on data protection and security as threats to the health care industry continue to evolve
**HITRUST CSF Certification, announced in July 2020, was effective December 2019. The scope of the certification covers Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan’s Electronic Data Interchange system and infrastructure.
Blue Distinction Centers for Substance Use Treatment and Recovery: the newest BDC designation
As you may have read in our provider publications earlier this year, the Blue Distinction® Specialty Care program added a new Blue Distinction® Center designation for Substance Use Treatment and Recovery, effective January 2020.
Blue Distinction Centers are nationally designated facilities that show a commitment to delivering improved patient safety and better health outcomes, based on objective measures that were developed with input from the community and leading accreditation and quality organizations. The BDC Substance Use Treatment and Recovery program requires designated facilities to deliver coordinated multidisciplinary care to patients and provide timely access to quality medical and psychosocial care in all phases of treatment.
Designated facilities must also offer medication-assisted treatment — a method of treating opioid addiction that includes a medication component as well as behavioral therapies.
Since the new designation was announced, three substance use treatment and recovery facilities in Michigan have been designated. Additional Michigan facilities are expected to be added to the program over the next year.
Programs like this are important as they provide another tool in the fight against the opioid epidemic. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 130 Americans die every day from an opioid overdose, a statistic that highlights the seriousness of the opioid crisis and how crucial it is for patients to receive comprehensive care.
In addition to this new designation, the Blue Distinction Specialty Care program is helping people find quality specialty care in the areas of bariatric surgery, cancer care, cardiac care, cellular immunotherapy, fertility care, gene therapy, knee and hip replacements, maternity care, spine surgery and transplants.
For more information
Updates on sequestration and DRG enhancement for Medicare Advantage providers
Earlier this year, the federal CARES Act implemented temporary sequestration relief and inpatient diagnosis-related group enhancement for Original Medicare payments. Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network applied this financial relief to our Medicare Advantage plans (Medicare Plus Blue℠ and BCN Advantage℠) for both network and non-network providers. We told you about this in an April web-DENIS alert, a June Record article and a July-August BCN Provider News article (Page 10).
Here are updates on those two temporary changes.
Temporary sequestration relief scheduled to end
At the time of this publication, the federal government has scheduled temporary sequestration relief to run through Dec. 31, 2020, dates of service. Blue Cross and BCN will re-implement sequestration in accordance with its provider agreements. This is currently scheduled to happen Jan. 1, 2021. If the federal government amends the sequestration restoration date, Blue Cross and BCN will also do so to remain in alignment with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid reimbursement policy.
What this means for you
Given this change in CMS payment methodology, this means that for both professional and facility providers, all of the Medicare Advantage services that had a 2% reduction in the amount paid prior to May 1, 2020, dates of service due to sequestration will once again have the reduction applied beginning Jan. 1, 2021, or any date after that as amended by the federal government. As was our previous practice, the claims payment adjustment will remain consistent with CMS payment methodology in that it will be applied to claims after determining any applicable member deductible, copayment or other member liability.
Durable medical equipment, end-stage renal disease services and lab providers aren’t affected by sequestration.
DRG enhancements
The CARES Act includes a temporary 20% increase in the weighting factor for inpatient DRG payments for Medicare patients diagnosed with COVID-19.
This 20% increase applies to discharges occurring on or after the emergency declaration on Jan. 27, 2020, and is expected to continue until the public health emergency ends. Providers are expected to follow CMS guidance indicating that claims eligible for the temporary increase must have a positive COVID-19 laboratory test in the patient’s medical record effective for admissions on or after Sept. 1, 2020.
More information is available in the MLN Matters® article SE20015 updated Aug. 17, 2020.**
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network don’t own or control this website.
Reminder: We simplified your appeal process
Effective Oct. 1, 2020, Provider Inquiry will verbally accept your post-service claim appeal requests. You may contact a representative at one of the telephone numbers below.
- Medical providers: 1-800-344-8525
- Facility providers: 1-800-249-5103
- Vision and hearing providers: 1-800-482-4047
For more information, see the previous article on this topic in the September Record.
Refer to the “Appeals and Problem Resolution” chapter of the PPO Provider Manual (located on web-DENIS) for a detailed overview of appeal filing criteria and guidelines.
Note: These changes only apply to Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan post-service commercial appeals. Blue Care Network commercial, BCN Advantage℠, Medicare Plus Blue℠, Medicare Private Fee for Service, Federal Employee Program® and Blue Cross Complete plans, as well as prior authorization and clinical editing appeals, aren’t affected by these changes.
Oct. 8 is National Depression Screening Day
Thursday, Oct. 8, is National Depression Screening Day**, a time for raising awareness about the importance of depression screening and treatment — and helping eliminate some of the stigma surrounding depression and other mental health issues.
More than 16 million (6.7%) adults in the U.S. suffer from major depression, according to Mental Health America.** Yet only a third (35.3%) of those suffering with severe depression seek appropriate treatment from a mental health professional.
“Depression is a chronic illness that often comes on so slowly that people may not even know they have it,” said Dr. William Beecroft, medical director of behavioral health for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network. “Screening for the condition, like screening for diabetes, is simple but people need to be aware of the signs of depression so they can seek help if needed.”
Blue Cross will be partnering with WLBY‑AM (Ann Arbor‑Ypsilanti), WOOD‑TV (Grand Rapids) and WTCM‑AM (Traverse City/Northern Lower Michigan) in advance of National Depression Screening Day to discuss the importance of depression screening. Andy Hetzel, vice president of Corporate Communications, will also discuss the topic on “Michigan’s Big Show” Oct. 6 with radio host Michael Patrick Shiels.
New Directions, a company that provides behavioral health services for most Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan members, has developed two flyers suitable for sharing with patients:
New Directions has also posted a series of depression guidelines** for members on its website.
Here are some other resources:
- We’ve posted materials related to depression and other mental health issues in the Mental Health Awareness section of the Blue Cross Engage page.
- For more mental health-related content, visit or subscribe to our blogs, A Healthier Michigan and MI Blues Perspectives. The Mind section of A Healthier Michigan has a wealth of information about depression, anxiety and how to end the stigma of mental health conditions.
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan doesn’t own or control this website.
Next Drug Take Back Day scheduled for Oct. 24
 Let your patients know that next National Prescription Drug Take Back Day is scheduled for Oct. 24 from 10 a.m. to 2 p.m. These twice-yearly events, coordinated by the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration, are a key tool in our efforts to battle the opioid epidemic. Let your patients know that next National Prescription Drug Take Back Day is scheduled for Oct. 24 from 10 a.m. to 2 p.m. These twice-yearly events, coordinated by the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration, are a key tool in our efforts to battle the opioid epidemic.
They provide a safe, convenient and responsible means of disposing of prescription drugs, while also educating the public about the potential for abuse of medications. At last October’s Drug Take Back Day, nearly 883,000 pounds of medication were collected nationwide.
As we’ve done previously, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan will support Drug Take Back Day in various ways. For example, we’ll post blogs on MI Blues Perspectives and offer resources on our Opioids 101 site.
To find a drug disposal facility near you that’s participating in Drug Take Back Day, check out the DEA’s search tool** or see Michigan OPEN’s Opioid Disposal Map.**
Keep in mind that people who miss the Take Back events don’t need to wait until the next event to safely dispose of unused drugs. For tips on how to safely dispose of unused drugs year-round, see the May 2018 Record article.
As a reminder, Meijer has a Consumer Drug Take-Back Program** in all Midwest stores. And you can dispose of unused prescription drugs at select Walgreens locations across the state. Read more about Blue Cross’ partnership with Walgreens by clicking here.
For more information on disposing of prescription drugs, visit the DEA Diversion Control Division website** or Michigan OPEN’s Opioid Disposal Information and Resources page.**
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan doesn’t own or control this website.
2020 third-quarter CPT code updates
Pathology and laboratory
Proprietary laboratory analysis codes
| Code |
Change |
Coverage comments |
Effective date |
| 0203U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0204U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0205U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0206U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0207U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0208U |
Added |
Covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0209U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0210U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0211U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0212U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0213U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0214U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0215U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0216U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0217U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0218U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0219U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0220U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0221U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
| 0222U |
Added |
Not covered |
Oct. 1, 2020 |
None of the information included in this article is intended to be legal advice and, as such, it remains the provider’s responsibility to ensure that all coding and documentation are done in accordance with all applicable state and federal laws and regulations.
Billing chart: Blues highlight medical, benefit policy changes
You’ll find the latest information about procedure codes and Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan billing guidelines in the following chart.
This billing chart is organized numerically by procedure code. Newly approved procedures will appear under the New Payable Procedures heading. Procedures for which we have changed a billing guideline or added a new payable group will appear under Updates to Payable Procedures. Procedures for which we are clarifying our guidelines will appear under Policy Clarifications. New procedures that are not covered will appear under Experimental Procedures.
You will also see that descriptions for the codes are no longer included. This is a result of recent negotiations with the AMA on use of the codes.
We will publish information about new BCBS groups or changes to group benefits under the Group Benefit Changes heading.
For more detailed descriptions of the BCBSM policies for these procedures, please check under the Medical/Payment Policy tab in Explainer on web-DENIS. To access this online information:
- Log in to web-DENIS.
- Click on BCBSM Provider Publications & Resources.
- Click on Benefit Policy for a Code.
- Click on Topic.
- Under Topic Criteria, click on the drop-down arrow next to Choose Identifier Type and then click on HCPCS Code.
- Enter the procedure code.
- Click on Finish.
- Click on Search.
| Code* |
BCBSM changes to:
Basic Benefit and Medical Policy, Group
Variations Payment Policy, Guidelines
|
| UPDATES TO PAYABLE PROCEDURES |
19318 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Reduction Mammaplasty for Breast-related Symptoms Policy
The safety and effectiveness of reduction mammoplasty have been established. It may be considered a useful therapeutic option (and not considered cosmetic) when one of the following guidelines is met:
- The patient meets specified patient selection guidelines.
- When performed in conjunction with medically necessary breast reconstruction for the purposes of attaining breast symmetry.
Criteria have been updated for this policy. The policy effective date is Sept. 1, 2020.
Inclusionary and exclusionary guidelines
Inclusions (must meet A, or must meet both B and C):
- Must meet both 1 and 2:
- Patient’s breasts are fully grown (i.e., breast size stable for approximately one year)
- Removal of more than 500 grams of tissue from each breast
- One of the following (1, 2 or 3) must be met:
- Pain (both of the following must be met)
- Documented pain in the neck or shoulders or postural backache, which must be of long-standing duration
- Failure of conservative therapy (e.g., an appropriate support bra, exercises, heat and cold treatments, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents or muscle relaxants)
- Shoulder grooving
- Recurrent intertrigo between the breasts and the chest wall
- Both of the following criteria must be met:
- Patient’s breasts are fully grown (i.e., breast size stable for approximately one year)
- The amount of tissue to be removed from each breast must be greater than or equal to the 22nd percentile on the Schnur Scale.**
**If one breast meets the tissue amount based on the Schnur Scale, even if the other breast does not, this criterion is met.
If one breast meets the Schnur scale criteria, and all other criteria for breast reduction are met, breast tissue may be removed from the other breast in order to achieve symmetry.
Exclusions:
Breast reduction isn’t covered for either of the following indications because it’s considered cosmetic in nature and not medically necessary:
- Surgery is being performed to treat psychological symptomatology or psychosocial complaints in the absence of significant physical, objective signs.
- Surgery is being performed for the sole purpose of improving appearance.
|
Established
36482, 36483
Experimental, not medically necessary
36473, 36474 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Endovenous Ablation for the Treatment of Varicose Veins (e.g., ClariVein®, VenaSeal™ Closure System) Policy
Procedure codes 36482 and 36483 are now payable for the endovenous ablation for the treatment of varicose veins (e.g., ClariVein®, VenaSeal™ Closure System) policy. The policy effective date is July 1, 2020.
Medical policy statement
Endovenous ablation of varicose veins by mechanochemical (ClariVein®) is experimental. This procedure hasn’t been scientifically demonstrated to be as safe and effective as conventional treatment.
Endovenous ablation of varicose veins by chemical adhesive (Cyanoacrylate, VenaSeal™) is established in patients with symptomatic varicose veins/venous insufficiency when the below criteria are met.
Inclusionary and exclusionary guidelines
Great or small saphenous veins
Cyanoacrylate adhesive may be considered established for symptomatic varicose veins/venous insufficiency when all the following criteria have been met:
- There is demonstrated saphenous reflux and clinical, etiology, anatomy and pathophysiology, or CEAP, class C2 or greater.
- There is documentation of one or more of the following indications:
- Ulceration secondary to venous stasis
- Recurrent superficial thrombophlebitis
- Hemorrhage or recurrent bleeding episodes from a ruptured superficial varicosity
- Persistent pain, swelling, itching, burning or other symptoms are associated with saphenous reflux, and the symptoms significantly interfere with activities of daily living, and conservative management including compression therapy for at least three months hasn’t improved the symptoms.
Accessory saphenous veins (all the following)
- Incompetence of the accessory saphenous vein is isolated or the great or small saphenous veins had been previously eliminated (at least three months).
- There is demonstrated accessory saphenous reflux.
- There is documentation of one or more of the following indications:
- Ulceration secondary to venous stasis
- Recurrent superficial thrombophlebitis
- Hemorrhage or recurrent bleeding episodes from a ruptured superficial varicosity
- Persistent pain, swelling, itching, burning, or other symptoms are associated with saphenous reflux, and the symptoms significantly interfere with activities of daily living, and conservative management including compression therapy for at least three months hasn’t improved the symptoms.
|
38204, 38205, 38207-38215, 38230, 38240, 38242, 38243, 81265-81268, 81370-81383, 86812, 86813, 86816, 86817, 86821, 86822 S2140, S2142, S2150
|
Basic benefit and medical policy
Bone Marrow Transplant ̶ Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Myeloproliferative Neoplasms, Allogeneic Policy
The safety and effectiveness of allogeneic HCT or reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic HCT have been established as a treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes or myeloproliferative neoplasms. It’s a useful therapeutic option for patients meeting selection criteria. The policy effective date is Sept. 1, 2020.
Inclusions:
Allogeneic HCT may be considered established as a treatment of one of the following:
- Myelodysplastic syndromes
- Myeloproliferative neoplasms
Reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic HCT may be considered established as a treatment of one of the following:
- Myelodysplastic syndromes
- Myeloproliferative neoplasms in patients who are at high-risk** of intolerance of a myeloablative conditioning regimen.
**Includes both age and comorbidities
Exclusions:
Patients not meeting the above diagnostic criteria. |
38208, 38211, 38212, 38213, 38214, 38215, 38232, 38241, 38243
Not covered:**
38204, 38205, 38206, 38207, 38209, 38210, 38230, 38240, 38242, 81267, 81268, 81370, 81371, 81372, 81373,
81374, 81375, 81376, 81377, 81378,
81379, 81380, 81381, 81382, 81383,
86812, 86813, 86816, 86817, 86821,
S2140, S2142, S2150
**Payable for other indications
|
Basic benefit and medical policy
Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Autoimmune Diseases Policy
Autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation may be considered a useful therapeutic option when indicated.
This policy is effective Sept. 1, 2020.
Inclusions:
Autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation as a treatment of systemic sclerosis/scleroderma when all the following are met:
- Condition is rapidly progressing and the prognosis is poor
- Internal organ involvement is indicated by one of the following:
- Cardiac involvement (for example, abnormal electrocardiogram)
- Pulmonary (both of the following):
- Evidence of interstitial lung disease (one of the following):
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Ground glass appearance on high-resolution chest CT
- Diffusing capacity of carbon monoxide, or DLCo, < 80% of predicted value or a decline of forced vital capacity (FVC) of ≥ 10% in last 12 months
- Renal: scleroderma-related renal disease
Exclusions:
- Treatment of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma):
- In severe organ involvement that is irreversible
- Not meeting the above criteria
- Autologous or allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation as a treatment of autoimmune diseases not listed above, including, but not limited to:
- Multiple sclerosis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Juvenile idiopathic and rheumatoid arthritis
- Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Crohn’s disease
- Immune cytopenia
- Relapsing polychondritis
|
J3490
J3590
|
Basic benefit and medical policy
Triferic AVNU (ferric pyrophosphate citrate)
Triferic AVNU (ferric pyrophosphate citrate) is payable when billed for FDA-approved indications, effective March 27, 2020. Triferic AVNU (ferric pyrophosphate citrate) should be reported with procedure code J3490 or J3590 and the appropriate national drug code until a permanent code is established.
URMBT groups are excluded from coverage of this drug.
Triferic AVNU (ferric pyrophosphate citrate) is an iron replacement product indicated for the replacement of iron to maintain hemoglobin in adult patients with hemodialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease, or HDD-CKD.
Dosage and administration:
6.75 mg iron (III) intravenously over three to four hours at each hemodialysis session via pre-dialyzer infusion line, post-dialyzer infusion line or a separate connection to the venous blood line. |
J9299 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Opdivo (nivolumab)
Opdivo (nivolumab), procedure code J9299, is payable for the updated FDA-approved indications. Effective April 1, 2020, indications have been updated to include patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who have been previously treated with sorafenib as a single agent or in combination with ipilimumab.
Effective May 1, 2020, indications were updated to include adult patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer expressing PD-L1(≥1%) as determined by an FDA-approved test, with no EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations, as first-line treatment in combination with ipilimumab. |
J9999 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Jelmyto (mitomycin)
Jelmyto (mitomycin) is payable when billed for FDA-approved indications, effective April 15, 2020. Jelmyto (mitomycin) should be reported with procedure code J9999 and the appropriate national drug code until a permanent code is established.
URMBT groups are excluded from coverage of this drug.
Jelmyto (mitomycin) is for pyelocalyceal use only and not for intravenous use, topical use or oral administration.
Administer 1.3 g of sodium bicarbonate orally the evening prior to, the morning of and 30 minutes prior to instillation procedure (total of 3.9 g).
The dose of Jelmyto to be instilled is 4 mg per mL via ureteral catheter or ephrostomy tube, with total instillation volume based on volumetric measurements using pyelography, not to exceed 15 mL (60 mg of mitomycin).
Instill Jelmyto once weekly for six weeks. For patients with a complete response three months after Jelmyto initiation, Jelmyto instillations may be administered once a month for a maximum of 11 additional instillations. |
| POLICY CLARIFICATIONS |
20999**
**Unclassified code used to report service |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Coblation®, Radiofrequency Ablation for Musculoskeletal Conditions Policy
The clinical utility of Coblation, or cold radiofrequency ablation for musculoskeletal conditions, hasn’t been demonstrated. Radiofrequency ablation using Coblation technology for these indications is considered experimental, effective Sept. 1, 2020. |
40806, 40819, 41010, 41115, 41520 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Frenum Surgery (Frenulum Surgery, Frenyumectomy, Frenectomy, Frenotomy) Policy
The safety and effectiveness of surgery to the lingual (under the tongue) frenulum have been established. It may be considered a useful therapeutic option when the patient selection criteria are met.
The safety and effectiveness of surgery to the maxillary anterior labial (class III or IV) frenulum in the infant have been established. It may be considered a useful therapeutic option when the patient selection criteria are met.
The policy effective date is Sept. 1, 2020.
Inclusions:
Indications for ankyloglossia surgery (must meet one):
- There is documentation of an infant’s inability to adequately breast or bottle feed due to ineffective latch.
- Physical examination of a child (may be as young as 9 months of age) by a qualified medical provider confirms the presence of “tongue tie,” causing difficulty in the child’s speech due to the inability to manipulate the tongue. For example, the child may be unable to protrude his tongue past his lips, which would impair his speech.
- Speech therapy evaluation confirms expressive language difficulties as a result of tongue immobility.
Indications for midline maxillary labial frenum surgery (must meet one):
- An infant with a history of not gaining weight
- There is documentation of an infant’s inability to adequately breast or bottle feed due to ineffective latch
- A mother experiencing painful breastfeeding
- Class III lip-tie: frenum inserts between the areas where the maxillary incisors erupt
- Class IV lip-tie: the frenum wraps into the hard palate and into the anterior papilla
Exclusions:
- Services that are dental in nature
- Routine frenulum (clipping) surgery at the time of delivery of the newborn
|
43229
43270
|
Basic benefit and medical policy
Endoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation or Cryoablation for Barrett Esophagus Policy
The safety and effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation for high- and low-grade dysplasia in Barrett esophagus have been established. It may be a useful therapeutic option when indicated.
Radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of Barrett esophagus is experimental when the below criteria aren’t met, including, but not limited to, Barrett esophagus in the absence of dysplasia. While this procedure may be safe, its effectiveness for this clinical indication hasn’t been established.
Cryoablation for Barrett esophagus, with or without dysplasia, is experimental. While this procedure may be safe, its effectiveness for this clinical indication hasn’t been established. The policy effective date is Sept. 1, 2020.
Inclusions:
- Radiofrequency ablation for Barrett esophagus with high-grade dysplasia may be used alone or in combination with endoscopic mucosal resection of nodular/visible lesions.
- Radiofrequency ablation for Barrett esophagus with low-grade dysplasia may be used when the initial diagnosis of LGD is confirmed by two pathologists with expertise in gastrointestinal histopathology.
Exclusions:
- Radiofrequency for Barrett esophagus in the absence of dysplasia
- Cryoablation for Barrett esophagus, with or without dysplasia
|
43499**
**Unlisted code used to report service
|
Basic benefit and medical policy
POEM for Esophageal Achalasia or Gastroparesis Policy
Peroral endoscopic myotomy, known as POEM, as a treatment for pediatric and adult esophageal achalasia or gastroparesis is experimental. It hasn’t been scientifically demonstrated to be as safe and effective as conventional treatment, effective Sept. 1, 2020. |
76499**
**Not otherwise classified code used to report service
|
Basic benefit and medical policy
Intraoperative Fluorescence Imaging Systems Policy
Assessment of vascular patency, tissue viability or organ identification or perfusion by any technology (e.g., Artemis Handheld Imaging Systems, Fluobeam 800, Infrared 800, Leica FL800, PDE-Neo, SPY Fluorescent Imaging System, VS3 Iridium System) is considered an incidental part of the procedure when clinical utility has been demonstrated (e.g., breast reconstruction, choroid blood flow, parathyroid perfusion, to aid in sentinel lymph node biopsy) and is not separately reimbursable, effective May 1, 2020. |
81210, 81235, 81275, 81276, 81404, 81405, 81406, 81479 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Circulating Tumor DNA for Management of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (Liquid Biopsy) Policy
The effectiveness and clinical utility of circulating tumor DNA for management of non-small-cell lung cancer (liquid biopsy) has been established. It may be considered a useful therapeutic option when indicated.
Inclusions:
Analyzing cell-free/circulating tumor DNA, or ctDNA, alterations in the ALK, EGFR, BRAF V600E, KRAS, ROS1, NTRK, MET exon14 skipping and RET gene when all the following apply:
- Advanced stage III or IV non-small-cell lung cancer
- Clinical circumstances reflect one of the following:
- Patient is medically unfit for invasive tissue sampling
- Following pathologic confirmation of a NSCLC diagnosis there is insufficient material for molecular analysis
- Follow-up tissue-based analysis is planned for all patients in which an oncogenic driver isn’t identified
- Used to detect ctDNA for targeted therapy benefit or to identify patients who won’t benefit from further molecular testing
Exclusions:
- Use of circulating tumor DNA for any indications not mentioned above
This policy is effective Sept. 1, 2020. |
90651 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Gardasil 9 (Human Papillomavirus 9-valent Vaccine, Recombinant)
Effective June 23, 2020, Gardasil 9 (Human Papillomavirus 9-valent Vaccine, Recombinant) is payable for the following updated indications:
Gardasil 9 (Human Papillomavirus 9-valent Vaccine, Recombinant) is indicated for the following new indication:
Gardasil 9 is a vaccine indicated in girls and women ages 9 through 45 for the prevention of the following diseases:
- Cervical, vulvar, vaginal, anal, oropharyngeal and other head and neck cancers caused by HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52 and 58
Gardasil 9 is indicated in boys and men ages 9 through 45 for the prevention of the following diseases:
- Anal, oropharyngeal and other head and neck cancers caused by HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52 and 58
And the following precancerous or dysplastic lesions caused by HPV types 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52 and 58:
The oropharyngeal and head and neck cancer indication is approved under accelerated approval based on effectiveness in preventing HPV-related anogenital disease. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
Limitations of use and effectiveness:
- Vaccination with Gardasil 9 doesn’t eliminate the necessity for vaccine recipients to undergo screening for cervical, vulvar, vaginal, anal, oropharyngeal and other head and neck cancers, as recommended by a health care provider.
- Not all vulvar, vaginal, anal, oropharyngeal and other head and neck cancers are caused by HPV, and Gardasil 9 protects only against those vulvar, vaginal, anal, oropharyngeal and other head and neck cancers caused by HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52 and 58.
- Gardasil 9 isn’t a treatment for external genital lesions; cervical, vulvar, vaginal, anal, oropharyngeal and other head and neck cancers; CIN, VIN, VaIN or AIN.
|
99183, G0277
Not covered (experimental):
A4575, E0446
|
Basic benefit and medical policy
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Policy
The safety and effectiveness of systemic hyperbaric oxygen therapy have been established for some conditions. It may be considered a useful therapeutic option when indicated for specified conditions.
Topical hyperbaric oxygen therapy is experimental. It hasn’t been scientifically demonstrated to improve patient clinical outcomes.
The policy has been updated, effective Sept. 1, 2020.
Inclusions:
Note: For some contracts, hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be excluded when performed in the office setting. Check with carrier for location restrictions.
The following conditions are effectively treated by systemic hyperbaric oxygen therapy:
- Acute peripheral arterial insufficiency
- Acute traumatic peripheral ischemia: HBOT is a valuable adjunctive treatment to be used in combination with accepted standard therapeutic measures when loss of function, limb or life is threatened
- Carbon monoxide poisoning/intoxication, acute
- Chronic refractory osteomyelitis, unresponsive to conventional medical and surgical management
- Crush injuries and suturing of severed limbs as an adjunctive treatment when loss of function, limb or life is threatened
- Cyanide poisoning, acute
- Decompression illness
- Diabetic wounds of the lower extremities in patients who meet all the following criteria:
- A diagnosis of Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes with a lower extremity wound that is due to diabetes
- A wound classified as Wagner grade 3 or higher
- The Wagner classification system of wounds is defined as follows:
- Grade 0 — No open lesion
- Grade 1 — Superficial ulcer without penetration to deeper layers
- Grade 2 — Ulcer penetrates to tendon, bone, or joint
- Grade 3 — Lesion has penetrated deeper than grade 2 and there is abscess, osteomyelitis, pyarthrosis, plantar space abscess, or infection of the tendon and tendon sheaths
- Grade 4 — Wet or dry gangrene in the toes or forefoot
- Grade 5 — Gangrene involves the whole foot or such a percentage that no local procedures are possible and amputation (at least at the below the knee level) is indicated.)
- The patient has failed an adequate course of standard wound therapy. Standard wound care in patients with diabetic wounds includes all the following:
- The assessment of a patient’s vascular status and correction of any vascular problems in the affected limb if possible
- The optimization of nutritional status
- Optimization of glucose control
- Debridement by any means to remove devitalized tissue
- Maintenance of a clean, moist bed of granulation tissue with appropriate moist dressings
- Appropriate off-loading
- Necessary treatment to resolve any infection that might be present.
- Gas embolism, acute
- Gas gangrene (i.e., clostridial myonecrosis)
- Non-diabetic wounds:
- There is no measurable sign of healing for at least 30 consecutive days or when there is failure to respond to standard wound care.
- Wounds must be evaluated at least every 30 days during administration of HBOT for measurable signs of improvement. (See exclusion criteria)
- Osteoradionecrosis as an adjunct to conventional treatment
- Pre and post treatment for patients undergoing dental surgery (non-implant related) of an irradiated jaw
- Preparation and preservation of compromised skin grafts (not for primary management of wounds)
- Profound anemia with exceptional blood loss: only when blood transfusion is impossible or must be delayed
- Progressive necrotizing infections
- Refractory mycoses: mucormycosis, actinomycosis, Conidiobolus coronata only as an adjunct to conventional therapy when the disease process is refractory to antibiotics and surgical treatment**
- Soft-tissue radiation necrosis (e.g., radiation enteritis, cystitis, proctitis) as an adjunct to conventional treatment
**For several of the indications included, there is little published evidence to support the effectiveness of hyperbaric oxygen therapy. However, there is little likelihood of RCTs being done for such relatively rare indications. Generally, these patients present with clinically severe situations where therapeutic options are limited. Subject matter expert experience and limited available evidence support that hyperbaric oxygen treatment may offer therapeutic benefit in these cases.
Wounds, including diabetic wounds, being treated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy must be reviewed using clinical documentation that identifies measurable signs of healing, e.g., width, depth and length of the wound.
Exclusions:
- Topical hyperbaric oxygen therapy
- Hyperbaric oxygen pressurization is considered experimental in the treatment of the following conditions (this list may not be all-inclusive):
- Acute coronary syndromes and as an adjunct to coronary interventions, including but not limited to percutaneous coronary interventions and cardiopulmonary bypass
- Acute or chronic cerebral vascular insufficiency
- Acute ischemic stroke
- Acute osteomyelitis, refractory to standard medical management
- Acute thermal and chemical pulmonary damage, i.e., smoke inhalation with pulmonary insufficiency
- Acute surgical and traumatic wounds
- Arthritic diseases
- Autism spectrum disorders
- Bell palsy
- Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw
- Bone grafts
- Brown recluse spider bites
- Carbon tetrachloride poisoning, acute
- Cardiogenic shock
- Cerebral edema; acute
- Cerebral palsy
- Cerebrovascular disease, acute (thrombotic or embolic) or chronic
- Chronic arm lymphedema following radiotherapy for cancer
- Chronic peripheral vascular insufficiency
- Chronic wounds, other than those situations under the inclusions
- Cosmetic use
- Delayed onset muscle soreness
- Demyelinating diseases, e.g., multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Fibromyalgia
- Fracture healing
- Hepatic necrosis
- Herpes zoster
- Hydrogen sulfide poisoning
- Idiopathic femoral neck necrosis
- Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss
- Inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn disease or ulcerative colitis)
- Intra-abdominal and intracranial abscesses
- In vitro fertilization
- Lepromatous leprosy
- Meningitis
- Mental illness (i.e., posttraumatic stress disorder, generalized anxiety disorder or depression)
- Migraine
- Motor dysfunction associated with stroke
- Multiple sclerosis
- Myocardial infarction
- Non-diabetic wounds
- Continued treatment should be discontinued when there are no measurable signs of healing within any 30-day period of treatment. (See inclusions.)
- Nonvascular causes of chronic brain syndrome (Pick’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, Korsakoff’s disease)
- Organ storage
- Organ transplantation
- Pseudomembranous colitis (antimicrobial agent-induced colitis)
- Pulmonary emphysema
- Pyoderma gangrenosum
- Radiation-induced injury in the head and neck, except as noted under the inclusions
- Retinal artery insufficiency, acute
- Retinopathy, adjunct to scleral buckling procedures in patients with sickle cell peripheral retinopathy and retinal detachment
- Senility
- Septicemia, aerobic
- Septicemia (anaerobic) and infection other than clostridial
- Severe or refractory Crohn’s disease
- Sickle cell crisis and/or hematuria
- Skin burns (thermal), acute
- Spinal cord injury
- Tetanus
- Traumatic brain injury
- Tumor sensitization for cancer treatments, including but not limited to, radiotherapy or chemotherapy
- Vascular dementia
|
J3090 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Sivextro (tedizolid phosphate)
Effective June 19, 2020, Sivextro (tedizolid phosphate) is payable for pediatric patients 12 years and older in alignment with the updated FDA indications.
Sivextro (tedizolid phosphate) is an oxazolidinone-class antibacterial drug indicated in adult and pediatric patients 12 years and older for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections, or ABSSSI, caused by designated susceptible bacteria.
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Sivextro and other antibacterial drugs, Sivextro should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria.
Dosage and administration:
Administer 200 mg once daily orally or as an intravenous infusion over one hour for six days in adult and pediatric patients 12 years and older. |
J3490
J3590 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Lyumjev (insulin lispro-aabc)
Lyumjev (insulin lispro-aabc) is considered established, effective June 15, 2020.
Lyumjev is a rapid-acting human insulin analog indicated to improve glycemic control in adults with diabetes mellitus.
Dosage and administration (See full prescribing information for important administration instructions)
- Subcutaneous injection:
- Administer Lyumjev at the start of a meal or within 20 minutes after starting a meal subcutaneously into the abdomen, upper arm, thigh or buttocks.
- Rotate injection sites within the same region to reduce risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis.
- Should generally be used in regimens with an intermediate or long-acting insulin.
- Intravenous infusion:
- Administer Lyumjev U-100 intravenously only under medical supervision.
- Dilute Lyumjev U-100 to a concentration of 1 unit/mL.
- Individualize and adjust the dosage of Lyumjev based on the patient’s metabolic needs, glucose monitoring results and glycemic control goal.
- Dose adjustments may be needed when switching from another insulin, with changes in physical activity, changes in concomitant medications, changes in meal patterns (i.e., amount and type of food, timing of food intake), changes in renal or hepatic function, or during acute illness.
This drug isn’t a benefit for URMBT. |
J3490
J3590 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Nyvepria (pegfilgrastim-apgf)
Effective June 10, 2020, Nyvepria (pegfilgrastim-apgf) is covered for the following FDA-approved indications:
Nyvepria (pegfilgrastim-apgf) is a leukocyte growth factor indicated to decrease the incidence of infection, as manifested by febrile neutropenia, in patients with non-myeloid malignancies receiving myelosuppressive anti-cancer drugs associated with a clinically significant incidence of febrile neutropenia.
Limitations of use:
Nyvepria isn’t indicated for the mobilization of peripheral blood progenitor cells for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
Dosage and administration:
Patients with cancer receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy.
- 6 mg administered subcutaneously once per chemotherapy cycle.
- Don’t administer between 14 days before and 24 hours after administration of cytotoxic chemotherapy.
- Use weight-based dosing for pediatric patients weighing less than 45 kg.
This drug isn’t a benefit for URMBT. |
J3490
J3590 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Sevenfact (factor VIIa)
Effective April 1, 2020, Sevenfact (factor VIIa) is covered for the following FDA-approved indications:
Sevenfact (coagulation factor VIIa [recombinant]-jncw) is a coagulation factor VIIa concentrate indicated for the treatment and control of bleeding episodes occurring in adults and adolescents (ages 12 and older) with hemophilia A or B with inhibitors.
Type of bleeding
Dosing regimen recommendation for mild or moderate bleeds, one of the following:
- 75 mcg/kg repeated every three hours until hemostasis is achieved
- Initial dose of 225 mcg/kg. If hemostasis isn’t achieved within nine hours, additional 75 mcg/kg doses may be administered every three hours as need to achieve hemostasis
For severe bleeds dosing regimen recommendation:
- 225 mcg/kg, followed, if necessary, six hours later with 75 mcg/kg every two hours
Dosage forms and strengths
Sevenfact is available as a lyophilized powder in single-use vials containing 1 or 5 mg of coagulation factor VIIa (recombinant)-jncw. After reconstitution with a specified volume of sterile water for injection, each mL contains 1 mg (1,000 mcg) of coagulation factor VIIa (recombinant)-jncw.
This drug isn’t a benefit for URMBT. |
J3490
J3590 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Uplizna (inebilizumab-cdon)
Effective June 11, 2020, Uplizna (inebilizumab-cdon) is covered for the following FDA-approved indications:
Uplizna is a CD19-directed cytolytic antibody indicated for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder in adult patients who are anti-aquaporin-4, or AQP4, antibody positive.
Uplizna (inebilizumab-cdon) isn’t a benefit for URMBT. |
J9022 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Tecentriq (atezolizumab)
Effective May 18, 2020, Tecentriq (atezolizumab) is payable for the following updated indications:
Non-small-cell lung cancer, or NSCLC
- For the first-line treatment of adult patients with metastatic NSCLC whose tumors have high PD -L1 expression (PD-L1 stained ≥ 50% of tumor cells [TC ≥ 50%] or PD-L1 stained tumor-infiltrating immune cells [IC] covering ≥ 10% of the tumor area [IC ≥ 10%]), as determined by an FDA-approved test, with no EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Administer Tecentriq 1,200 mg, followed by 15 mg/kg bevacizumab on the same day every three weeks
- If bevacizumab is discontinued, administer Tecentriq as:
- 840 mg every two weeks, 1,200 mg every three weeks or 1,680 mg every four weeks
|
J9299 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Opdivo (nivolumab)
Effective May 26, 2020, Opdivo (nivolumab) is payable for the following updated indications:
- Adult patients with metastatic or recurrent non-small-cell lung cancer with no EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations as first-line treatment, in combination with ipilimumab and two cycles of platinum-doublet chemotherapy.
- Patients with unresectable advanced, recurrent or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma after prior fluoropyrimidine- and platinum-based chemotherapy.
|
J9999 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Phesgo (pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and hyaluronidase-zzxf)
Effective June 29, 2020, Phesgo (pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and hyaluronidase-zzxf) is covered for the following FDA-approved indications:
Phesgo is a combination of pertuzumab and trastuzumab, HER2/neu receptor antagonists, and hyaluronidase, an endoglycosidase, indicated for:
- Use in combination with chemotherapy as:
- Neoadjuvant treatment of patients with HER2-positive, locally advanced, inflammatory or early stage breast cancer (either greater than 2 cm in diameter or node positive) as part of a complete treatment regimen for early breast cancer.
- Adjuvant treatment of patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer at high risk of recurrence.
- Use in combination with docetaxel for treatment of patients with HER2positive metastatic breast cancer, or MBC, who haven’t received prior anti-HER2 therapy or chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
Dosage and administration:
- For subcutaneous use in the thigh only.
- Phesgo (pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and hyaluronidase-zzxf) has different dosage and administration instructions than intravenous pertuzumab and trastuzumab products.
- Don’t administer intravenously.
- Perform HER2 testing using FDA-approved tests by laboratories with demonstrated proficiency.
- The initial dose of Phesgo is 1,200 mg pertuzumab, 600 mg trastuzumab and 30,000 units hyaluronidase administered subcutaneously over approximately eight minutes, followed every three weeks by a dose of 600 mg pertuzumab, 600 mg trastuzumab and 20,000 units hyaluronidase administered subcutaneously over approximately five minutes.
- Neoadjuvant: Administer Phesgo by subcutaneous injection every three weeks and chemotherapy by intravenous infusion preoperatively for 3 to 6 cycles.
- Adjuvant: Administer Phesgo by subcutaneous injection every three weeks and chemotherapy by intravenous infusion postoperatively for a total of one year (up to 18 cycles).
- MBC: Administer Phesgo by subcutaneous injection and docetaxel by intravenous infusion every three weeks.
This drug isn’t a benefit for URMBT. |
J9308 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Cyramza (ramuciumab)
Effective May 29, 2020, Cyramza (ramuciumab) is covered for the following FDA-approved indications:
Cyramza is a human vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) antagonist indicated:
In combination with erlotinib, for first-line treatment of metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor, or EGFR, exon 19 deletions or exon 21 (L858R) mutations. |
J9999 |
Basic benefit and medical policy
Zepzelca (lurpinectedin)
Effective June 15, 2020, Zepzelca (lurpinectedin) is covered for the following FDA-approved indications:
Zepzelca is an alkylating drug indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic small cell lung cancer with disease progression on or after platinum-based chemotherapy.
Zepzelca (lurpinectedin) isn’t a benefit for URMBT. |
S2066, S2067, S2068, 11920, 11921, 11922, 19301, 19302, 19303, 19305, 19306, 19307, 19316, 19318, 19324, 19325, 19328, 19330, 19340, 19342, 19350, 19355, 19357, 19361, 19364, 19366, 19367, 19368, 19369, 19370, 19371, 19380, 19396, L8600,** C1789**
**May be a facility benefit
|
Basic benefit and medical policy
Reconstructive breast surgery and breast implants
The safety and effectiveness of breast implant and breast reconstruction procedures have been established. Insertion, removal and reinsertion of silicone gel or saline filled breast implants are established procedures for breast reconstruction and implant surgery when specific clinical criteria are met.
Criteria have been updated, effective Sept. 1, 2020.
Breast reconstruction
Inclusions:
Breast reconstruction on the affected breast or contralateral breast to achieve symmetry (reconstruction may include insertion or re-insertion of implants [silicone or saline], free flap, autologous tissue, latissimus dorsi flap or transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap, nipple tattooing or nipple reconstruction) for any of the conditions listed below:
- Congenital defects, such as breast agenesis
- Mastectomy (including radical, modified radical, subcutaneous, simple and partial) due to current diagnosis of breast cancer
- Mastectomy secondary to family or personal history of cancer of the breast
- Accidental injury or trauma to the breast(s)
Exclusions:
All other conditions.
Implants
Inclusions:
Implant removal for documented:
- Baker Class III contractures (only if the initial implant was for reconstructive purposes)
- Baker Class IV contracture
- Recurrent infection
- Extrusion
- Silicone implant rupture
- Surgery or radiation therapy for a new diagnosis of breast cancer
- Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma, or BIA-ALCL
- Suspected BIA-ALCL (symptoms of pain, swelling, redness or lump in the area of the implant; seroma; asymmetry of the breast)
- Bilateral removal is covered if requested
- Textured-surface breast implant, when the surgeon determines it is in the best interest of the patient
- Implants or tissue expanders that have been withdrawn from the market at the request of the FDA (e.g., Allergan BIOCELL®)
Exclusions:
The following indications for removal of breast implant are considered not medically necessary:
- Patient anxiety
- Pain not related to contractures or rupture
- Baker Class III contractures in patients with implants for cosmetic purposes
- Removal of a ruptured saline breast implant(s) when the original insertion was for a cosmetic purpose
- Systemic symptoms attributed to connective tissue diseases, autoimmune diseases, etc.
Please reference the table on the medical policy for detailed information regarding medical necessity. |
T1015
T1019
|
Basic benefit and medical policy
Starting Dec. 1, we’ll no longer pay for T1015, T1019
Effective Dec. 1, 2020, we’ll no longer be paying for procedure codes T1015 and T1019. In 2006, we began paying for these procedure codes as an introduction to achieve consistent delivery of evidence-based recommendations in caring for patients with chronic illness. Since Provider Delivered Care Management is payable for most of our groups and we don’t want to double pay for such services, the T codes are no longer needed. |

Direct reimbursement available to athletic trainers for physical medicine services on or after Jan. 1
Athletic trainers will have the opportunity to participate in Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan’s commercial networks (Traditional and TRUST), as well as BCN commercial and BCN Advantage℠, starting Jan. 1, 2021.
Participating athletic trainers will receive direct reimbursement for covered services within the scope of their licensure at 85% of the applicable fee schedule, minus any member deductibles and copayments. This change, effective for services provided on or after Jan. 1, affects Blue Cross and BCN benefit plans that cover services that these providers are licensed to provide. To find out if a patient has coverage, check web‑DENIS for member benefits and eligibility or call Provider Inquiry at 1‑800‑344‑8525.
Athletic trainers can apply for the networks starting Oct. 1, 2020. To apply, go to bcbsm.com/providers and click on Enroll to become a provider. Specific qualification requirements are identified within each agreement.
All applicants to the TRUST PPO, BCN HMO and BCN Advantage networks must pass a credentialing review before participation. We’ll notify applicants in writing of their approval status.
Authorization requests for BCN members
For BCN commercial and BCN Advantage members, athletic trainers must submit authorization requests for physical medicine services to eviCore healthcare. There is no authorization required for Blue Cross commercial members.
About PT benefits
Athletic trainers should tell members that the physical medicine services they provide count toward a member’s physical therapy benefits. Because PT benefits are limited during a plan year, the physical medicine services provided by athletic trainers will reduce a member’s future benefits for that plan year.
We’re covering acupuncture for Medicare Advantage members
Retroactive to Jan. 21, 2020, Medicare Plus Blue℠ and BCN Advantage℠ members have coverage for acupuncture to treat chronic low back pain, or cLBP. We cover up to 12 visits in 90 days for qualifying patients who’ve had chronic low back pain, defined as:
- Lasting 12 weeks or longer
- Nonspecific, in that it has no identifiable systemic cause (for example, not associated with metastatic, inflammatory or infectious disease)
- Not associated with surgery
- Not associated with pregnancy
We’ll cover eight additional visits for patients showing improvement, but no more than 20 visits annually. Treatment must be discontinued if the patient doesn’t improve or regresses.
Medicare doesn’t cover any type of acupuncture, including dry needling, for conditions other than cLBP.
Providers can offer this service if they meet all applicable educational and state licensing requirements. For more information on these requirements, refer to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ Decision Memo for Acupuncture for Chronic Low Back Pain.**
This decision is based on CMS’ National Coverage Determination for Acupuncture for Chronic Low Back Pain and doesn’t apply to Blue Cross or BCN commercial members.
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network don’t own or control this website.
We’re launching a new digital tool to help improve our members’ behavioral health
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan is committed to providing its customers and members with tools to help them deal with daily life stressors.
On Jan. 1, 2021, Blue Cross and Blue Care Network are launching Livongo for Behavioral Health by myStrength, a website and digital application product. It will be available for all fully insured groups with Blue Cross and BCN commercial coverage, as well as select self-funded groups.
With more than 1,600 activities, myStrength covers over 30 topics, including depression, anxiety, insomnia, substance use disorders, chronic pain, opioid use disorder, medication-assisted treatment, stress, mindfulness, balancing emotions, pregnancy and early parenting, nicotine use and trauma.
Based on their plans, members will have access to the following:
- Self-guided tools and videos for all Blue Cross and BCN fully insured groups
- Self-guided tools, videos and asynchronous engagement coaching for select Blue Cross and BCN self-funded groups.
Members can call the Customer Service number on the back of their member ID cards to determine whether they have access to the myStrength solution.
As a reminder, earlier this year in response to COVID-19, we worked with Livongo to offer a limited release of Livongo’s myStrength COVID-19 module to all our members at no cost through Dec. 31, 2020. After Dec. 31, members will no longer have access to this custom module.
To learn more about the myStrength solution, go to mystrength.com.**
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network don’t own or control this website.
Reminder: Preauthorization required for certain behavioral health services and concurrent reviews for Medicare Plus Blue PPO members
For Medicare Plus Blue℠ PPO members, behavioral health inpatient, partial hospitalization and intensive outpatient services continue to require preauthorization. To obtain preauthorization, providers must submit requests for initial admissions and extensions of treatment through e-referral.
This process excludes acute detoxification admissions, which should be processed as a medical service and follow the preauthorization requirements for regular inpatient admission. Outpatient behavioral health services for Medicare Plus Blue members don’t require prior authorization.
We use InterQual criteria to determine the medical necessity of the services. Cases that don’t meet criteria won’t be approved. Providers may obtain a copy of the criteria used to render all decisions. They can also speak with the behavioral health medical director regarding medical necessity decisions by calling Medicare Plus Blue Behavioral Health Services at 1-888-803-4960.
How do I appeal denied services?
Providers can appeal denied services by faxing an appeal request to 1-866-315-0442 or emailing the request to AABHMAPPO@bcbsm.com.
For peer-to-peer conversations with Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan behavioral health medical directors, call 1-877-293-2788 to discuss cases that don’t meet criteria for approval.
For more information, refer to the “Utilization management” chapter of the Medicare Plus Blue PPO Manual. Review the section titled “Preauthorization of behavioral health services.”
HEDIS® 2020 Medicare Advantage star measure changes
In July, the National Committee for Quality Assurance released proposed HEDIS® specification changes** for the 2020 measurement year. NCQA will receive comments regarding the proposed changes and release final specifications at the end of October.
We’re providing advance communication of important specification changes at this time.
Key updates:
Controlling high blood pressure (CBP)
New definition: Hypertensive patients ages 18 to 85 whose blood pressure is adequately controlled (<140/90) during the measurement year. The last blood pressure reading of the year determines compliance.
Important changes:
- Patients are now identified for the measure by two outpatient visits with a diagnosis of hypertension between Jan. 1 of the prior year and June 30 of the measure year.
- Blood pressure readings:
- Blood pressures taken by a patient from any digital device are acceptable as long as it’s documented in the patient’s legal record by the provider managing the patient’s blood pressure.
- Blood pressure readings taken by the patient using a non-digital device, such as a manual blood pressure cuff and a stethoscope, are not allowed for HEDIS reporting.
- Patient self-reported blood pressure readings may be obtained during telehealth, telephone, e-visits and virtual check-ins.
Submit claims with blood pressure CPT II code results even if the blood pressure isn’t compliant. Including CPT II result codes on the claim alleviates the need for a medical record request.
| CPT II code |
Most recent systolic blood pressure |
| *3074F |
<130 mm Hg |
| *3075 |
130–139 mm Hg |
| *3077F |
≥140 mm Hg |
| CPT II code |
Most recent diastolic blood pressure |
| *3078F |
<80 mm Hg |
| *3079F |
80–89 mm Hg |
| *3080F |
≥90 mm Hg |
Palliative care exclusion
Patients receiving palliative care are now excluded from the following measures:
- Breast cancer screening (BCS)
- Colorectal cancer screening (COL)
- Controlling high blood pressure (CBP)
- Comprehensive diabetes care (CDC)
- Statin therapy for patients with cardiovascular disease (SPC)
- Osteoporosis management in women who had a fracture (OMW)
Advanced illness exclusion
The following measures now allow advanced illness to be captured via telephone and e-visits:
- Breast cancer screening (BCS)
- Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug therapy for rheumatoid arthritis (ART)
- Colorectal cancer screening (COL)
- Controlling high blood pressure (CBP)
- Comprehensive diabetes care (CDC)
- Statin therapy for patients with cardiovascular disease (SPC)
- Osteoporosis management in women who had a fracture (OMW)
Telephone and e-visit claims with advanced illness diagnoses will exclude patients from the measure if all exclusion requirements are met:
- 66 and older (67 and older for OMW)
- Two advanced illness claims in the measurement year or the prior measurement year and a frailty code in the measurement year
Frailty codes are required for the advanced illness exclusion but cannot be obtained through telephone or e-visit claim.
**HEDIS® is a registered trademark of the National Committee for Quality Assurance.
Using telehealth to help close patient gaps in care
Many health care providers are using telehealth to provide care to sick patients. But did you know that you can also use telehealth to help meet your patients’ preventive care needs and provide treatment for patients with chronic conditions?
To help you understand how telehealth can assist you in closing gaps in your patients’ care, we created the Telehealth Summary of 2020 HEDIS® Measures.** This document summarizes how you can use telehealth for prevention and screening, care coordination, diabetes care and services for cardiovascular, respiratory, musculoskeletal and behavioral health conditions, among others.
Using this document can help you meet the requirements for HEDIS measures and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services star measures. In addition, the tips offered in this document can help eligible health care providers increase their performance in the Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network 2020 Quality Rewards program.
Here’s how to find the Telehealth Summary of 2020 HEDIS® Measures:
- Log in as a provider at bcbsm.com.
- Click on BCBSM Provider Publications and Resources.
- Click on Newsletters & Resources.
- Click on Clinical Quality Corner.
Other resources
Here are some other helpful resources:
- HEDIS, star and pharmacy measure tip sheets are available on the Clinical Quality Corner webpage. Follow the navigation instructions described above.
- The 2020 Quality Measure Description document is available in the Resources section of Health e‑Blue℠.
- The 2020 Quality Rewards Booklet is available in the Resources section of Health e‑Blue℠.
- Learn more about telehealth by clicking on the provider tab at bcbsm.com/coronavirus or logging in as a provider at bcbsm.com and clicking on Coronavirus (COVID-19).
**HEDIS®, which stands for Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set, is a registered trademark of the National Committee for Quality Assurance, or NCQA.
Encourage patients to get flu vaccine with help from CDC toolkit
Flu season is quickly approaching. And fewer than half of Americans get the flu vaccine — well below the national target of 70%, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
| Year |
2015-16 |
2016-17 |
2017-18 |
2018-19 |
| Percentage of U.S. adults who received a flu vaccine (ages 18 and older) |
41.7 |
43.3 |
37.1 |
45.3 |
| Percentage of U.S. children who received a flu vaccine (age 6 months through 17) |
59.3 |
59.0 |
57.9 |
62.6 |
During the 2018-2019 flu season, the CDC reported the flu vaccine prevented:
- 4.4 million flu illnesses
- 58,000 flu hospitalizations
- 3,500 flu deaths
A recommendation by a physician, nurse, pharmacist or other health care professional is one of the most important factors influencing a patient’s decision to get a flu vaccine, according to the CDC.
To help health care providers and their patients fight the flu, the CDC developed a Health Care Professional Fight Flu Toolkit** that includes:
- Educational materials for patients
- Appointment reminder email template
- Sample social media content
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan doesn’t own or control this website.
Reminder: Additional codes for influenza testing in a doctor’s office
Earlier this year, we added new CPT codes to our physician in-office laboratory procedures list. We added these codes to help physicians rule out influenza during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Here are the CPT codes for influenza tests that can now be performed in a physician’s office:
- *87275
- *87276
- *87400
- *87804
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan commercial and Medicare Plus Blue℠ plans already cover CPT code *87804. The remainder of the codes are new for the physician in-office laboratory procedures list. All four codes are covered in the physician’s office, with an effective date of Feb. 4, 2020, for the following lines of business:
- Blue Cross commercial
- Medicare Plus Blue
- Blue Care Network commercial
- BCN Advantage℠
Reminder: Guidelines for annual physicals
Under the terms of the Affordable Care Act, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network commercial members typically qualify for an annual physical.
Here are some other guidelines to keep in mind:
- Some members may qualify for more than one physical each year, depending on their age, sex and the type of plan they have.
- Government guidelines for commercial coverage don’t apply to members who are part of the Federal Employee Program®, Michigan Public School Employees’ Retirement System, UAW Retiree Medical Benefits Trust or other retiree or self-funded groups that don’t follow government rules.
- Members with one of our Medicare Advantage plans (Medicare Plus Blue℠ PPO or BCN Advantage℠) qualify for annual wellness visits. Those who are new to Medicare can receive a “welcome to Medicare” preventive visit. For more details, see the January Record article.
BCN
BCN recently changed the frequency for preventive screenings to a calendar year for its commercial members to align with Blue Cross PPO plans and to allow members who deferred their screenings due to COVID-19 to have more flexibility in future scheduling.
This means members can schedule their routine screenings at any time during the year regardless of when they had the screening in the previous year. This applies to preventive screenings that members schedule annually, such as mammograms.
As a reminder, health care providers can schedule a physical for BCN members any time throughout the year. There are no limits to the frequency of physicals for HMO patients.
For more information, see the article on Page 1 of the September – October issue of BCN Provider News.
Medicare Advantage
BCN Advantage℠ and Medicare Plus Blue℠ PPO follow guidelines set by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. More information on the frequency of Medicare screenings is available at cms.gov.**
Benefits and eligibility
Because of variations in coverage, it’s always best to check benefits and eligibility for your patients on web-DENIS.
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network don’t own or control this website.
Inpatient admission requests submitted through e-referral for commercial members may be subject to clinical review
Starting Oct. 5, 2020, inpatient acute care admissions for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan commercial members submitted through e-referral could be subject to clinical review. It’s a process that our facilities already follow for Medicare Plus Blue℠ inpatient acute care admissions and some other members.
As part of our inpatient review program, select facilities must submit medical inpatient stays through e-referral. The stays may be reviewed and approved or pended for review by a clinician.
Behavioral health authorization requests and clinical reviews will continue according to the current process with the assigned behavioral health management company, working in conjunction with Blue Cross. However, inpatient admission authorization requests processed through New Directions, a company that provides behavioral health services for most Blue Cross members, will be subject to full clinical review from the first day of admission and subject to non-approval.
We’ve notified the affected facilities that their inpatient medical and behavioral health admissions require this new clinical review process.
Why we use clinical reviews
Clinical reviews are necessary to help customers determine ways to reduce the amount they spend on medical services and help us consistently apply utilization management programs. These reviews also help ensure that the patient stays are appropriate and billed correctly based on the patient’s diagnosis and condition.
Blue Care Network and our Medicare Advantage plans already have full inpatient review programs at Michigan hospitals.
If you’re not familiar with e-referral, please see the table below for available online training dates (each training is one hour):
| Date |
Time |
Registration link |
Hospital type |
| Tuesday, Oct. 6 |
11 a.m. |
Register |
Non-DRG** |
| Wednesday, Oct. 7 |
1 p.m. |
Register |
Non-DRG** |
| Tuesday, Oct. 13 |
1 p.m. |
Register |
DRG** |
| Wednesday, Oct. 14 |
11 a.m. |
Register |
DRG** |
**Diagnosis related group |
RC Claim Assist tool ensures correct billing units on medical drug codes
To help you bill claim units more easily, use the RC Claim Assist tool. It’s available to all contracted providers at no cost.
As electronic billing at the National Drug Code unit level becomes more of an industry standard, it’s still important that the HCPCS/CPT units align with the NDC units billed. RC Claim Assist can help you make quick and easy conversions from NDC dose to HCPCS or CPT units to help you correctly submit medical drug claims.
Steps to follow to complete a units conversion
- Enter the NDC code.
- Select the drug reimbursement code.
- Select the unit of measure to convert by:
- NDC pricing units
- Administered dose
- NDC package size
- HCPCS/CPT code units
- Enter the number administered.
- View the NDC conversion summary report (see screenshot below).
- View the average wholesale price, or AWP, displayed below the NDC billable units.
Tips to help you use the RC Claim Assist tool
- You can use any of these starting points to retrieve the conversion between HCPCS/CPT and NDC:
- HCPCS or CPT code
- NDC code
- Drug name
- Refer to the tool only as a general reference and in conjunction with other resources, such as applicable fee schedules.
- Note: AWP displayed is for reference only and doesn’t reflect the actual reimbursement in claims processing.
How do I access RC Claim Assist?
Go to the RC Claim Assist login page. You’ll register to use RC Claim Assist by following these steps:
- Enter your national provider identifier and click on Submit.
- Enter your first and last name.
- You’ll then be prompted to create a unique password.
You can find more information, including an instructional video, on the RC Claim Assist website under the About tab.
About National Drug Code quantities and conversions
- See the December 2018 Record for general guidelines for billing injectable drugs.
- See the May 2019 Record for tips on how to calculate and bill NDC quantities and tips on billing electronically.
For additional information on this tool so you can more quickly and easily convert HCPCS or CPT units to NDC units, see the September 2017 Record.
Update your Provider Authorization form when changes occur
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan is dedicated to safeguarding the protected health information of our members. These safeguards include a completed Trading Partner Agreement and Provider Authorization form as part of the electronic data interchange setup process. All EDI trading partners must complete a TPA and Provider Authorization form before they can exchange PHI with Blue Cross.
Terms of the TPA require you to notify Blue Cross of any changes in your trading partner information. If you switch service bureaus (clearinghouses), software vendors, billing services or the recipient for your 835 files, you must update your Provider Authorization form. Updating the form ensures information is routed to the appropriate destination. You don’t need to update the Provider Authorization form if your submitter and Trading Partner IDs don’t change.
Keep these items in mind when changes occur. You should review your Provider Authorization information if you’ve:
- Joined a new group practice
- Left a group practice and now bill using your own NPI
- Hired a new billing service
- Started submitting claims through a clearinghouse or you’ve changed clearinghouses
- Decided you no longer want to receive 835 remittance files
- Selected a new destination for your 835s
You must update your Provider Authorization form if you’ll be sending claims using a different submitter ID or routing your 835s to a different unique receiver or Trading Partner ID. To make changes to your EDI setup, visit bcbsm.com/providers and follow these steps:
- Click on Quick Links.
- Click on Electronic Connectivity (EDI).
- Click on How to use EDI to exchange information with us electronically.
- Click on Update your Provider Authorization Form under EDI Agreements.
If you have questions about EDI enrollment, contact the EDI Help Desk at 1-800-542-0945. For assistance with the TPA and Provider Authorization form, select the TPA option.
Sign up for additional training webinars
Provider Experience is continuing its series of training webinars for health care providers and staff. The webinars are designed to help you work more efficiently with Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network.
Here’s information on the upcoming training webinars:
| Webinar name |
Date and time |
Registration link |
| Blue Cross 201 — Claims Troubleshooting |
Thursday, Nov. 5, 2020
10 to 11 a.m. |
Click here to register. |
| Blue Cross 201 — Claims Troubleshooting |
Thursday, Nov. 5, 2020
2 to 3 p.m. |
Click here to register. |
| Blue Cross 201 — Claims Troubleshooting |
Wednesday, Nov. 11, 2020
10 to 11 a.m. |
Click here to register. |
| Blue Cross 201 — Claims Troubleshooting |
Wednesday, Nov. 11, 2020
2 to 3 p.m. |
Click here to register. |
The Blue Cross 201 webinar provides an in-depth learning opportunity and builds on information shared in our Blue Cross 101: Understanding the Basics webinar. This session reviews the processes and tools available when resolving common issues with claims.
Recordings of previous webinars are available on web-DENIS via the Blue Cross Provider Publications and Resources or BCN Provider Publications and Resources pages as follows.
Blue Cross Provider Publications and Resources
- Log in to Provider Secured Services.
- Click on BCBSM Provider Publications and Resources.
- Click on BCBSM Newsletters and Resources.
- Click on Provider Training.
- In the Featured Links section of the page, check out 2020 Provider Training Webinars.
You can also get more information about online training, presentations and videos by clicking on the E‑Learning icon at the top of the page.
BCN Provider Publications and Resources
- Log in to Provider Secured Services.
- Go to BCN Provider Publications and Resources.
- Under Other Resources, click on Learning Opportunities.
- Find the most recent webinars under 2020 Provider Training Webinars.
As additional training webinars become available, we’ll provide notices through web-DENIS, The Record and BCN Provider News.

We’re covering acupuncture for Medicare Advantage members
Retroactive to Jan. 21, 2020, Medicare Plus Blue℠ and BCN Advantage℠ members have coverage for acupuncture to treat chronic low back pain, or cLBP. We cover up to 12 visits in 90 days for qualifying patients who’ve had chronic low back pain, defined as:
- Lasting 12 weeks or longer
- Nonspecific, in that it has no identifiable systemic cause (for example, not associated with metastatic, inflammatory or infectious disease)
- Not associated with surgery
- Not associated with pregnancy
We’ll cover eight additional visits for patients showing improvement, but no more than 20 visits annually. Treatment must be discontinued if the patient doesn’t improve or regresses.
Medicare doesn’t cover any type of acupuncture, including dry needling, for conditions other than cLBP.
Providers can offer this service if they meet all applicable educational and state licensing requirements. For more information on these requirements, refer to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ Decision Memo for Acupuncture for Chronic Low Back Pain.**
This decision is based on CMS’ National Coverage Determination for Acupuncture for Chronic Low Back Pain and doesn’t apply to Blue Cross or BCN commercial members.
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network don’t own or control this website.
Reminder: Preauthorization required for certain behavioral health services and concurrent reviews for Medicare Plus Blue PPO members
For Medicare Plus Blue℠ PPO members, behavioral health inpatient, partial hospitalization and intensive outpatient services continue to require preauthorization. To obtain preauthorization, providers must submit requests for initial admissions and extensions of treatment through e-referral.
This process excludes acute detoxification admissions, which should be processed as a medical service and follow the preauthorization requirements for regular inpatient admission. Outpatient behavioral health services for Medicare Plus Blue members don’t require prior authorization.
We use InterQual criteria to determine the medical necessity of the services. Cases that don’t meet criteria won’t be approved. Providers may obtain a copy of the criteria used to render all decisions. They can also speak with the behavioral health medical director regarding medical necessity decisions by calling Medicare Plus Blue Behavioral Health Services at 1-888-803-4960.
How do I appeal denied services?
Providers can appeal denied services by faxing an appeal request to 1-866-315-0442 or emailing the request to AABHMAPPO@bcbsm.com.
For peer-to-peer conversations with Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan behavioral health medical directors, call 1-877-293-2788 to discuss cases that don’t meet criteria for approval.
For more information, refer to the “Utilization management” chapter of the Medicare Plus Blue PPO Manual. Review the section titled “Preauthorization of behavioral health services.”
Inpatient admission requests submitted through e-referral for commercial members may be subject to clinical review
Starting Oct. 5, 2020, inpatient acute care admissions for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan commercial members submitted through e-referral could be subject to clinical review. It’s a process that our facilities already follow for Medicare Plus Blue℠ inpatient acute care admissions and some other members.
As part of our inpatient review program, select facilities must submit medical inpatient stays through e-referral. The stays may be reviewed and approved or pended for review by a clinician.
Behavioral health authorization requests and clinical reviews will continue according to the current process with the assigned behavioral health management company, working in conjunction with Blue Cross. However, inpatient admission authorization requests processed through New Directions, a company that provides behavioral health services for most Blue Cross members, will be subject to full clinical review from the first day of admission and subject to non-approval.
We’ve notified the affected facilities that their inpatient medical and behavioral health admissions require this new clinical review process.
Why we use clinical reviews
Clinical reviews are necessary to help customers determine ways to reduce the amount they spend on medical services and help us consistently apply utilization management programs. These reviews also help ensure that the patient stays are appropriate and billed correctly based on the patient’s diagnosis and condition.
Blue Care Network and our Medicare Advantage plans already have full inpatient review programs at Michigan hospitals.
If you’re not familiar with e-referral, please see the table below for available online training dates (each training is one hour):
| Date |
Time |
Registration link |
Hospital type |
| Tuesday, Oct. 6 |
11 a.m. |
Register |
Non-DRG** |
| Wednesday, Oct. 7 |
1 p.m. |
Register |
Non-DRG** |
| Tuesday, Oct. 13 |
1 p.m. |
Register |
DRG** |
| Wednesday, Oct. 14 |
11 a.m. |
Register |
DRG** |
**Diagnosis related group |
Update your Provider Authorization form when changes occur
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan is dedicated to safeguarding the protected health information of our members. These safeguards include a completed Trading Partner Agreement and Provider Authorization form as part of the electronic data interchange setup process. All EDI trading partners must complete a TPA and Provider Authorization form before they can exchange PHI with Blue Cross.
Terms of the TPA require you to notify Blue Cross of any changes in your trading partner information. If you switch service bureaus (clearinghouses), software vendors, billing services or the recipient for your 835 files, you must update your Provider Authorization form. Updating the form ensures information is routed to the appropriate destination. You don’t need to update the Provider Authorization form if your submitter and Trading Partner IDs don’t change.
Keep these items in mind when changes occur. You should review your Provider Authorization information if you’ve:
- Joined a new group practice
- Left a group practice and now bill using your own NPI
- Hired a new billing service
- Started submitting claims through a clearinghouse or you’ve changed clearinghouses
- Decided you no longer want to receive 835 remittance files
- Selected a new destination for your 835s
You must update your Provider Authorization form if you’ll be sending claims using a different submitter ID or routing your 835s to a different unique receiver or Trading Partner ID. To make changes to your EDI setup, visit bcbsm.com/providers and follow these steps:
- Click on Quick Links.
- Click on Electronic Connectivity (EDI).
- Click on How to use EDI to exchange information with us electronically.
- Click on Update your Provider Authorization Form under EDI Agreements.
If you have questions about EDI enrollment, contact the EDI Help Desk at 1-800-542-0945. For assistance with the TPA and Provider Authorization form, select the TPA option.
Sign up for additional training webinars
Provider Experience is continuing its series of training webinars for health care providers and staff. The webinars are designed to help you work more efficiently with Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network.
Here’s information on the upcoming training webinars:
| Webinar name |
Date and time |
Registration link |
| Blue Cross 201 — Claims Troubleshooting |
Thursday, Nov. 5, 2020
10 to 11 a.m. |
Click here to register. |
| Blue Cross 201 — Claims Troubleshooting |
Thursday, Nov. 5, 2020
2 to 3 p.m. |
Click here to register. |
| Blue Cross 201 — Claims Troubleshooting |
Wednesday, Nov. 11, 2020
10 to 11 a.m. |
Click here to register. |
| Blue Cross 201 — Claims Troubleshooting |
Wednesday, Nov. 11, 2020
2 to 3 p.m. |
Click here to register. |
The Blue Cross 201 webinar provides an in-depth learning opportunity and builds on information shared in our Blue Cross 101: Understanding the Basics webinar. This session reviews the processes and tools available when resolving common issues with claims.
Recordings of previous webinars are available on web-DENIS via the Blue Cross Provider Publications and Resources or BCN Provider Publications and Resources pages as follows.
Blue Cross Provider Publications and Resources
- Log in to Provider Secured Services.
- Click on BCBSM Provider Publications and Resources.
- Click on BCBSM Newsletters and Resources.
- Click on Provider Training.
- In the Featured Links section of the page, check out 2020 Provider Training Webinars.
You can also get more information about online training, presentations and videos by clicking on the E‑Learning icon at the top of the page.
BCN Provider Publications and Resources
- Log in to Provider Secured Services.
- Go to BCN Provider Publications and Resources.
- Under Other Resources, click on Learning Opportunities.
- Find the most recent webinars under 2020 Provider Training Webinars.
As additional training webinars become available, we’ll provide notices through web-DENIS, The Record and BCN Provider News.

RC Claim Assist tool ensures correct billing units on medical drug codes
To help you bill claim units more easily, use the RC Claim Assist tool. It’s available to all contracted providers at no cost.
As electronic billing at the National Drug Code unit level becomes more of an industry standard, it’s still important that the HCPCS/CPT units align with the NDC units billed. RC Claim Assist can help you make quick and easy conversions from NDC dose to HCPCS or CPT units to help you correctly submit medical drug claims.
Steps to follow to complete a units conversion
- Enter the NDC code.
- Select the drug reimbursement code.
- Select the unit of measure to convert by:
- NDC pricing units
- Administered dose
- NDC package size
- HCPCS/CPT code units
- Enter the number administered.
- View the NDC conversion summary report (see screenshot below).
- View the average wholesale price, or AWP, displayed below the NDC billable units.

Tips to help you use the RC Claim Assist tool
- You can use any of these starting points to retrieve the conversion between HCPCS/CPT and NDC:
- HCPCS or CPT code
- NDC code
- Drug name
- Refer to the tool only as a general reference and in conjunction with other resources, such as applicable fee schedules.
- Note: AWP displayed is for reference only and doesn’t reflect the actual reimbursement in claims processing.
How do I access RC Claim Assist?
Go to the RC Claim Assist login page. You’ll register to use RC Claim Assist by following these steps:
- Enter your national provider identifier and click on Submit.
- Enter your first and last name.
- You’ll then be prompted to create a unique password.
You can find more information, including an instructional video, on the RC Claim Assist website under the About tab.
About National Drug Code quantities and conversions
- See the December 2018 Record for general guidelines for billing injectable drugs.
- See the May 2019 Record for tips on how to calculate and bill NDC quantities and tips on billing electronically.
For additional information on this tool so you can more quickly and easily convert HCPCS or CPT units to NDC units, see the September 2017 Record.
Pharmacies can bill us for COVID-19 testing
Pharmacies that participate in the Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network Vaccine Affiliation Program or have the ability to submit Medicare Part B medical claim forms can bill Blue Cross or BCN for COVID-19 testing services for patients with Blue Cross or BCN commercial or Medicare Advantage (Medicare Plus Blue℠ or BCN Advantage℠) coverage.
This change is in accordance with guidance issued April 8, 2020, by the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services** and Executive Order 2020-104 issued by Michigan Gov. Gretchen Whitmer.** It’s in effect until further notice.
Blue Cross and BCN are making it easier for members to get COVID-19 diagnostic and antibody tests by giving them more options on where they can be tested when:
- It’s medically necessary.
- The test is ordered by an attending health care provider.
The provider can be a licensed physician, pharmacist or attending clinician operating within the scope of their license.
We posted more information about this change in August on the COVID-19 webpage and on web-DENIS. A list of codes that pharmacies can use to bill COVID-19 testing is available on our COVID-19 webpages in the Patient testing section.
More information about COVID-19 testing is available on our public website at bcbsm.com/coronavirus and through the COVID-19 information page within Provider Secured Services.
**Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network don’t own or control this website.

Blue Cross updates its microprocessor-controlled knee medical policy
Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan updated its medical guidelines for its Microprocessor-Controlled Prostheses and Orthoses for the Lower Limb Policy, effective Sept. 1, 2020.
This update is for the following HCPCS codes:
- L5856
- L5857
- L5858
- L5973
- L2006
A microprocessor-controlled knee may be considered established in individuals with transfemoral amputation who meet all the following requirements:
- Demonstrated need for long distance ambulation at variable rates (use of the limb in the home or for basic community ambulation isn’t sufficient to justify provision of the computerized limb over standard limb applications) or demonstrated patient need for regular ambulation on uneven terrain or for regular use on stairs (Use of the limb for limited stair climbing in the home or employment environment is not sufficient evidence for prescription of this device over standard prosthetic application.)
- Physical ability, including adequate cardiovascular and pulmonary reserve, for ambulation at faster than normal walking speed
- Adequate cognitive ability to master use and care requirements for the technology
A microprocessor-controlled knee is considered established when individuals meet the below criteria.
A powered knee is considered experimental.
A microprocessor-controlled knee-ankle-foot, or KAF, device (e.g., Ottobock C-Brace™ Orthotronic Mobility System, Ottobock the Sensor Walk™ stance control KAFO) is considered experimental.
Inclusionary and exclusionary guidelines
Patient selection and identification
For patients in whom the potential benefits of the microprocessor knees are uncertain, patients may first be fitted with a standard prosthesis to determine their level of function with the standard device.
- Contraindications for the use of the microprocessor knee should include the following:
- Any condition that prevents socket fitting, such as a complicated wound or intractable pain that precludes socket wear
- Inability to tolerate the weight of the prosthesis
- Medicare level K0 — No ability or potential to ambulate or transfer
- Medicare level K1 — Limited ability to transfer or ambulate on level ground at fixed cadence
- Medicare level K2 — Limited community ambulator who doesn’t have the cardiovascular reserve, strength and balance to improve stability in stance to permit increased independence, less risk of falls and potential to advance to a less restrictive walking device
- Inability to use swing and stance features of the knee unit
- Poor balance or ataxia that limits ambulation
- Significant hip flexion contracture (greater than 20 degrees)
- Significant deformity of remaining limb that would impair the ability to stride
- Limited cardiovascular or pulmonary reserve or profound weakness
- Limited cognitive ability to understand gait sequencing or care requirements
- Long distance or competitive running
- Falls outside of recommended weight or height guidelines of the manufacturer
- Specific environmental factors, such as excessive moisture or dust, or inability to charge the prosthesis
- Extremely rural conditions where maintenance ability is limited
- Indications for the use of the microprocessor knee should include the following:
- Adequate cardiovascular and pulmonary reserve to ambulate at variable cadence
- Adequate strength and balance in stride to activate the knee unit
- Shouldn’t exceed the weight or height restrictions of the device
- Adequate cognitive ability to master technology and gait requirements of the device
- Hemi-pelvectomy through knee-disarticulation level of amputation, including bilateral; lower-extremity amputees are candidates if they meet functional criteria as listed
- The patient is an active walker and requires a device that reduces energy consumption to permit longer distances with less fatigue
- Daily activities or job tasks that don’t permit full focus of concentration on knee control and stability, such as uneven terrain, ramps, curbs, stairs, repetitive lifting or carrying
- Medicare level K2 — Limited community ambulator, but only if improved stability in stance permits increased independence, less risk of falls and potential to advance to a less restrictive walking device, and the patient has cardiovascular reserve, strength and balance to use the prosthesis. The microprocessor enables fine-tuning and adjustment of the hydraulic mechanism to accommodate the unique motor skills and demands of the functional level K2 ambulator.
- Medicare level K3 — Unlimited community ambulator
- Medicare level K4 — Active adult, athlete who needs to function as a K3 level in daily activities
- Potential to lessen back pain by providing more secure stance control, using less muscle control to keep the knee stable
- Potential to unload and decrease stress on remaining limb
- Potential to return to an active lifestyle
- Physical and functional fitting criteria for new amputees:
- New amputees may be considered if they meet certain criteria as outlined above
- Premorbid and current functional assessment important determinant
- Requires stable wound and ability to fit the socket
- Must have potential to return to an active lifestyle
The above guidelines come from the Veterans Health Administration Prosthetic Clinical Management Program Clinical Practice Recommendations for Microprocessor Knees (Berry, 2000).
|




 We are pleased to announce that Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan has received HITRUST CSF® Certification.
We are pleased to announce that Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan has received HITRUST CSF® Certification. Let your patients know that next National Prescription Drug Take Back Day is scheduled for Oct. 24 from 10 a.m. to 2 p.m. These twice-yearly events, coordinated by the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration, are a key tool in our efforts to battle the opioid epidemic.
Let your patients know that next National Prescription Drug Take Back Day is scheduled for Oct. 24 from 10 a.m. to 2 p.m. These twice-yearly events, coordinated by the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration, are a key tool in our efforts to battle the opioid epidemic.